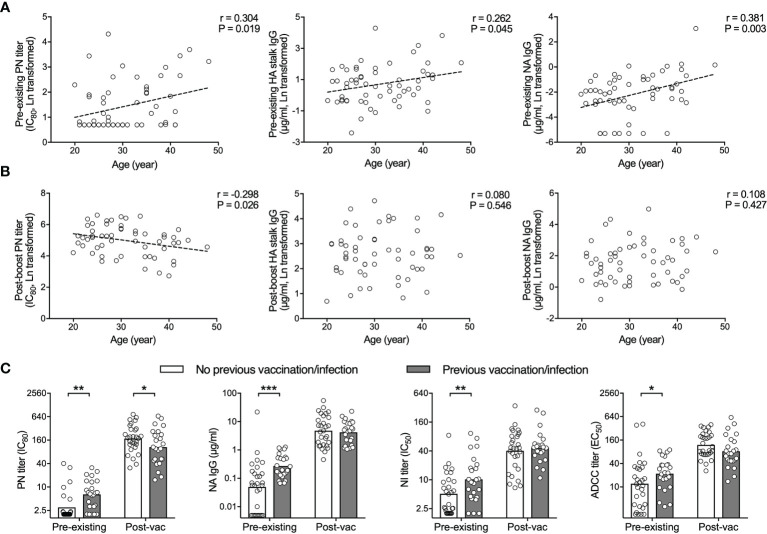
Figure 3.
H5N1 vaccines elicit potent antibody responses regardless of pre-existing humoral immunity. (A, B) HA specific neutralizing antibodies (PN titer, left), total HA stalk specific antibodies (IgG, center) and total NA specific antibodies (IgG, right) tested in pre-vaccination sera (pre-existing, D0, A) correlate with age. Inverse or no significant correlation with age is found in sera after vaccination (post-vac, D42, B). (C) Subjects with previous vaccination and/or infection had significantly higher pre-existing antibodies, compared to subjects without previous vaccination or infection. After vaccination, the difference was abolished. HA specific neutralizing antibodies (PN titer, far left), total NA specific antibodies (IgG, central left), neuraminidase enzymatic activity inhibiting antibodies (NI titer, central right), and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) inducing antibodies (ADCC titer, far right) were tested in sera before (pre-existing) and 42 days after vaccination (post-vac). The geometric mean titers are shown as bars (C), and each symbol represents one subject (A–C). Linear fitting curve was plotted as dotted line when Pearson correlation P < 0,05. Pearson r and P values are noted for each correlation (A, B). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Antibody titers and concentrations were Ln transformed in statistical analyses. Fisher’s LSD test between subjects with previous vaccination/infection and subjects without was performed in two-way ANOVA in (C).