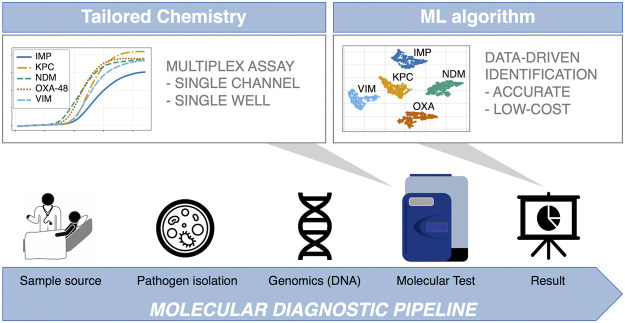
FIGURE 1.
Integration of data-driven approaches to standard diagnostic workflows. The blue arrow indicates the conventional diagnosis pipeline from patient to result, where patient sample is collected from different sources (e.g., eye swab, nasopharyngeal swab, throat swab, urine, or rectal swab). Subsequently, samples are cultured, and nucleic acids are extracted in a microbiology lab. Following this, the most suitable genetic test is developed in-silico, comprising of specialised assays capable of multi target detection in a single reaction (first grey arrow). The test is performed in the dPCR instrument, outputting large amounts of data, which are analysed by a machine learning supported algorithm to ensure reliable and accurate results (second grey arrow). This is where the AMCA methodology is applied.