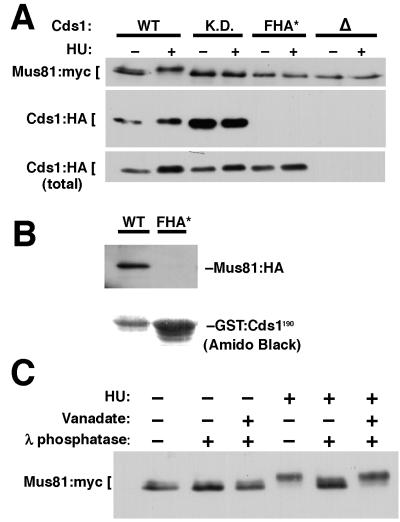
FIG. 2.
Mus81 and Cds1 associate in vivo. (A) Cells that expressed Mus81:myc and Cds1:HA from genomic loci were treated (+) or not treated (−) with HU. Immunoprecipitation with myc antibodies showed that Mus81:myc coprecipitated with Cds1:HA (WT) and Cds1 kinase dead (K.D.) but not with the Cds1 FHA mutant (FHA*). A Cds1 deletion strain (▵) served as a control. The bottom panel (total) is an immunoblot of Cds1:HA present in samples prior to immunoprecipitation. Note that lower-mobility forms of Mus81:myc were detected only in wild-type cells. (B) The 1-to-190 region of the Cds1 wild type (WT) or the FHA mutant (FHA*) was expressed from the nmt1 promoter as a GST fusion protein (GST:Cds1190) in a Mus81:HA strain. GST:Cds1190 proteins were purified and detected with amido black or immunoblotted with antibodies to HA. Mus81:HA coprecipitated with the wild-type but not with the mutant FHA domain. (C) Mus81 is a phosphoprotein. A Mus81:13myc strain was treated with HU (+) or not treated. (−) A Mus81:myc strain was immunoprecipitated and treated with λ phosphatase (+) or not treated, (−) either with (+) or without (−) the phosphatase inhibitor vanadate.