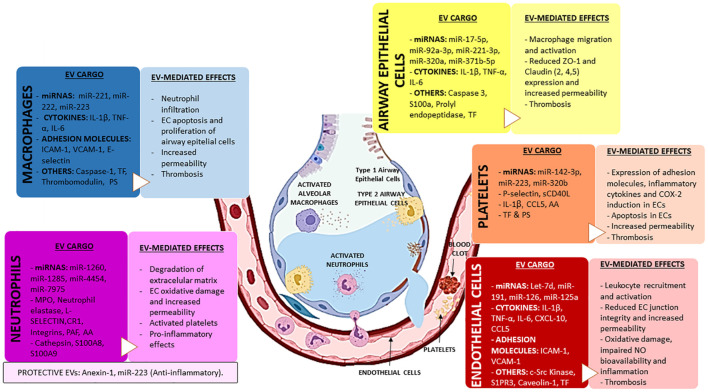
FIGURE 1.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) involved in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Schematic representation of an injured alveolus in ARDS and the potential role of specific EVs based on their parent cell and their cargo. AA, Arachidonic acid; CCL5, C-C motif chemokine 5 (also known as RANTES); CR1, Complement Receptor-1; CXCL-10, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; EC, endothelial cells; IL, interleukin; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; miR, micro ribonucleic acid; NO, nitric oxide; PAF, platelet activating factor; PS, phosphatidylserine; S100A8, S100 calcium-binding protein A8; S100A9, S100 calcium-binding protein A9; S1PR3, Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 3; sCD40L, soluble CD40 ligand; TF, tissue factor; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor-α; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion protein 1; ZO-1, zonula occludens-1. This figure was created with BioRender.com.