FIGURE 1. Structure of a ROR family ECR.
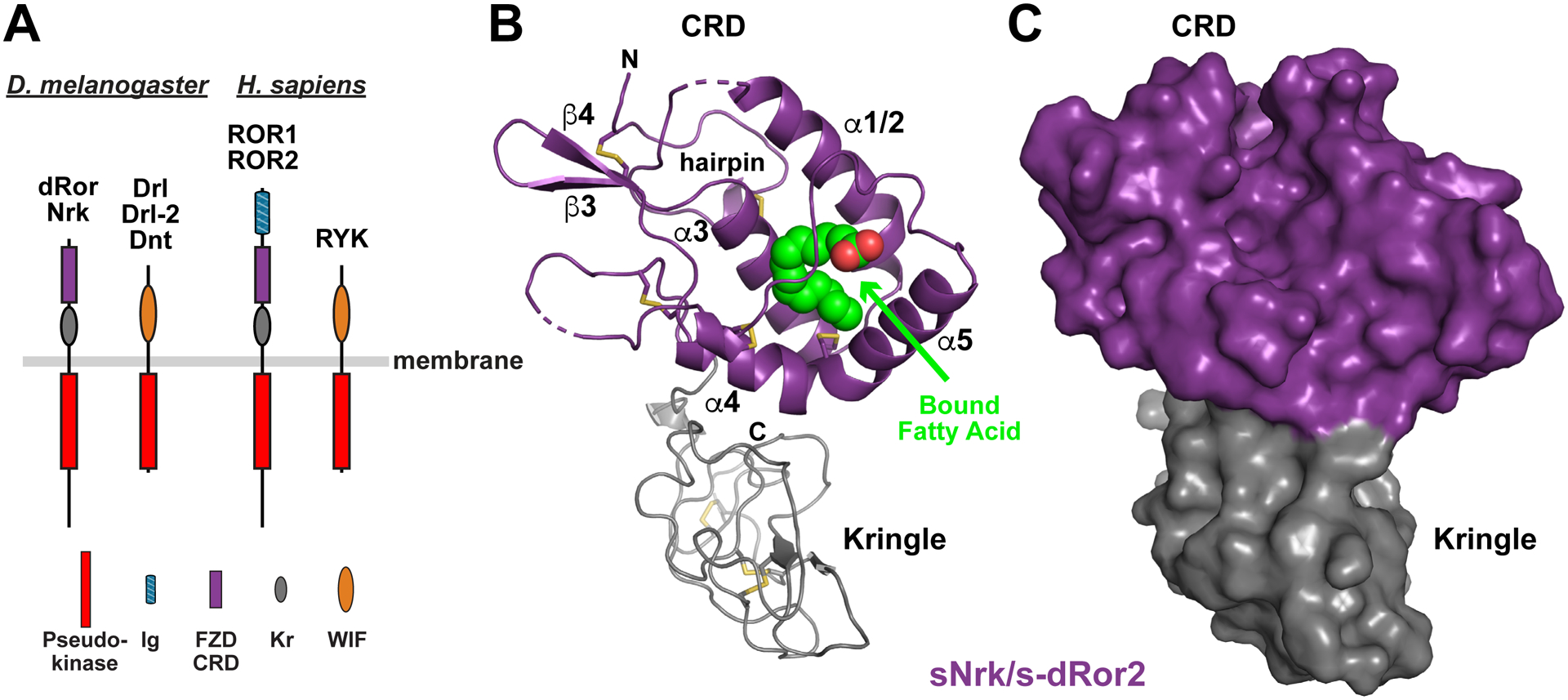
(A) Domain composition of ROR and RYK/Drl family RTKs from D. melanogaster (left) and H. sapiens (right). The membrane is depicted as a horizontal gray bar. The pseudokinase domain is red, immunoglobulin-like domain blue, FZD-related CRD purple, Kringle domain grey, and WIF domain orange. Note that there are three RYK orthologs in D. melanogaster, but only one in humans.
(B) Cartoon representation of the sNrk/s-dRor2 structure, with the CRD colored purple and Kringle domain grey. Secondary structure elements are labeled in the CRD only – using the designation introduced by the Leahy lab (Dann et al., 2001) – and the bound fatty acid molecule is shown as green and red spheres. Disulfides are shown as sticks, and the N-terminal hairpin is marked.
(C) Surface representation of sNrk/s-dRor2, colored as in B. Note that burial of the bound fatty acid molecule causes it not to be visible at all in this representation.
See also Figure S1.
