Figure 4.
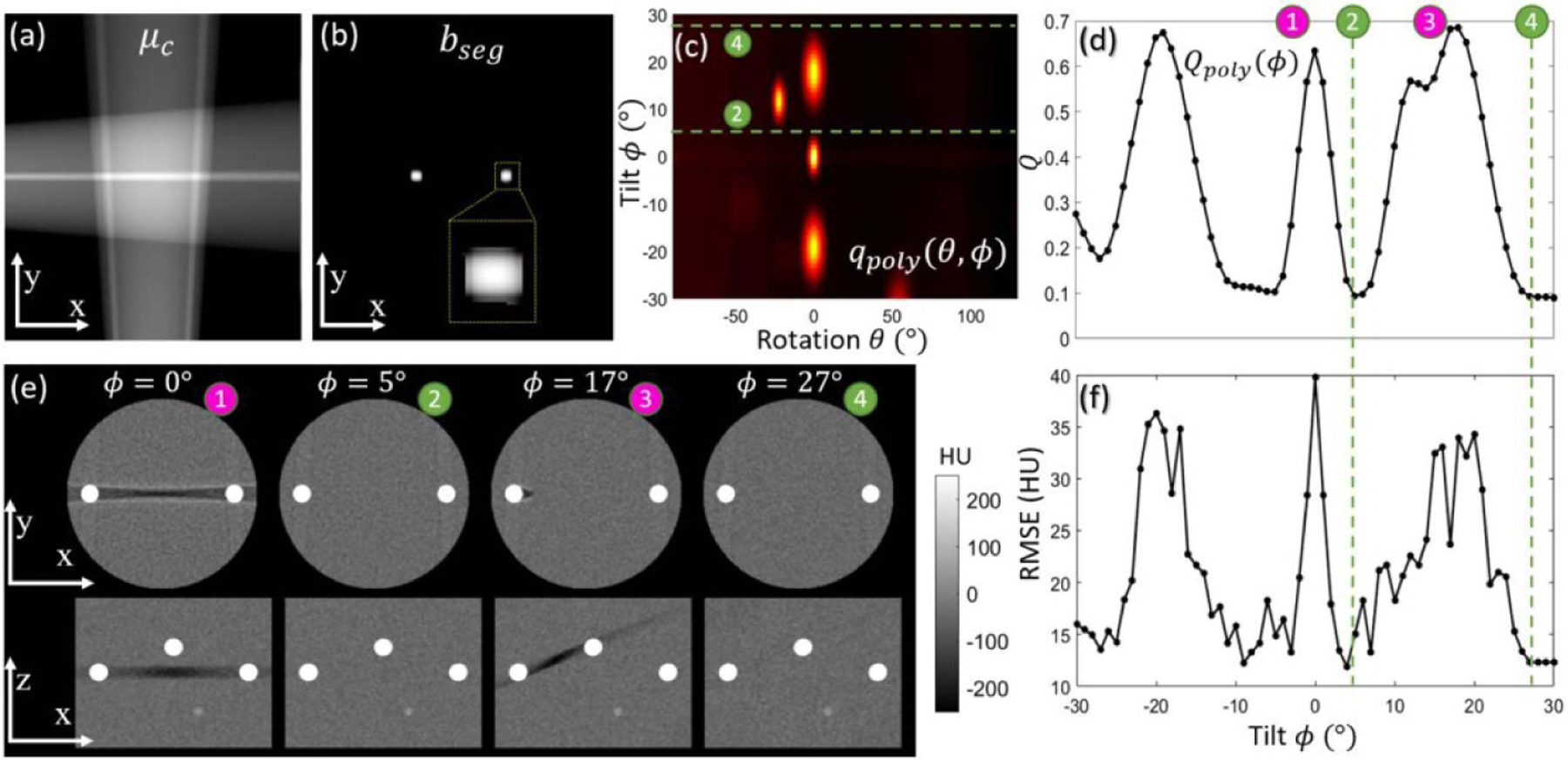
Study #1: Simulation study involving a water cylinder with a variety of metal spheres and rods. (a) Coarse attenuation map μc computed from 2 scout views. The central axial (x, y) plane is shown, recognizing that the coarse attenuation map is computed over the full 3D volume. (b) Segmentation bseg computed by the U-Net. (c) Metric map qpoly (θ, ϕ) computed over a realistic range of rotation (θ) and tilt (ϕ) angles. Optimal tilted semi-circular orbits are marked by dashed green lines labeled ➁ and ➃, which avoid projection views with high spectral shift. (d) Objective function Qpoly (ϕ) computed from equation (5). (e) Axial and sagittal slices from FBP image reconstructions of data acquired at various tilt angles. (f) The RMSE analyzed as a function of tilt angle ϕ is seen to follow a similar trend as the objective function in (d), confirming the basic notion that minimization of variation in spectral shift (from qpoly (θ, ϕ)) minimizes metal artifacts in 3D image reconstructions.
