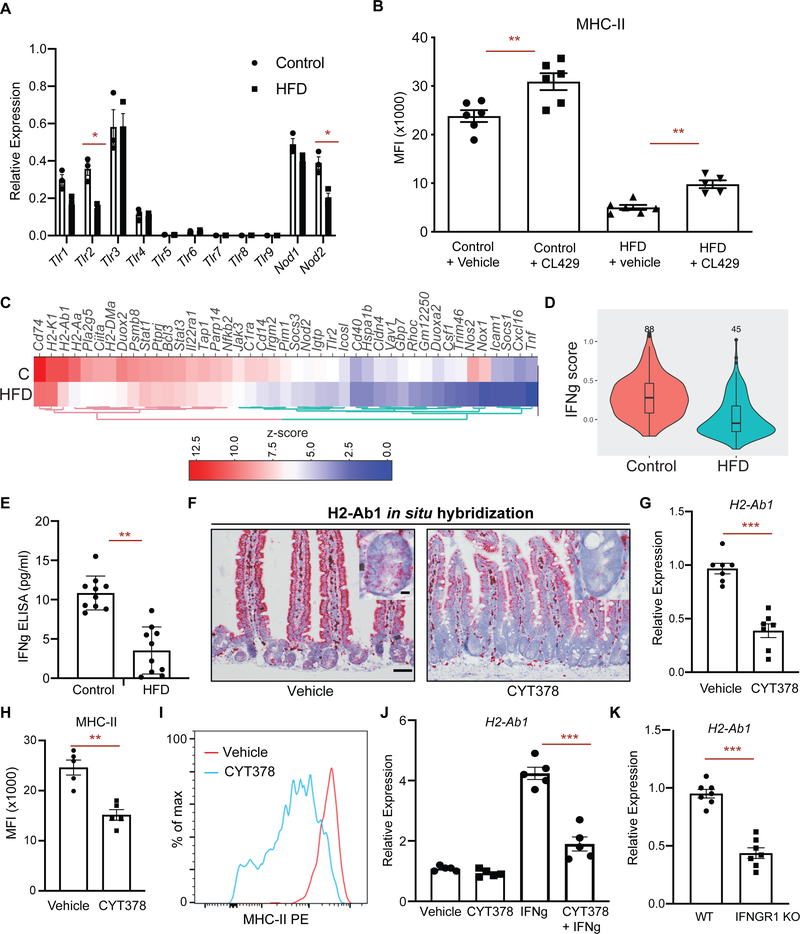
Figure 5 |. PRR and IFN γ signaling regulate epithelial MHC-II expression.
A. Relative expression of pattern recognition receptors (PRR) in control and HFD ISCs (n=3).
B. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of MHC-II in Lgr5+ ISCs from vehicle- and TLR2/NOD2 agonist CL429− treated control and HFD mice (n=6 mice, mean ± s.e.m.).
C. A heat map of expression levels of IFN γ-induced genes between HFD and control Lgr5+ ISCs by bulk RNA-seq (n=2). Scale represents computed z-scores of log10 expression values.
D. Violin plots demonstrating the expression levels of IFN γ-induced genes in control and HFD Lgr5+ ISCs by scRNA-seq.
E. IFN γ levels in the intestines of control and HFD mice as measured by ELISA (n=10, mean ± s.e.m.).
F. In situ hybridization for H2-Ab1 in vehicle- and JAK1/2 & TBK1/IKKε inhibitor (CYT387)-treated mice in small intestine (n=3).
G. Relative expression of MHC-II (H2-Ab1) in Lgr5+ ISCs from vehicle- and CYT387-treated mice (n=7, mean ± s.e.m.).
H, I. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of MHC-II in Lgr5+ ISCs from vehicle- and CYT387-treated mice (H, n=5, mean ± s.e.m.). Representative flow cytometry histogram plots of MHC-II expression in Lgr5+ ISCs (I).
J. Relative expression of MHC-II (H2-Ab1) in intestinal organoids-treated with or without CYT387 and/or IFN γ (n=5, mean ± s.e.m.).
K. Relative expression of MHC-II (H2-Ab1) in Epcam+ cells isolated from crypts of control or IFNGR1 KO (n=5, mean ± s.e.m.).
*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t-tests).