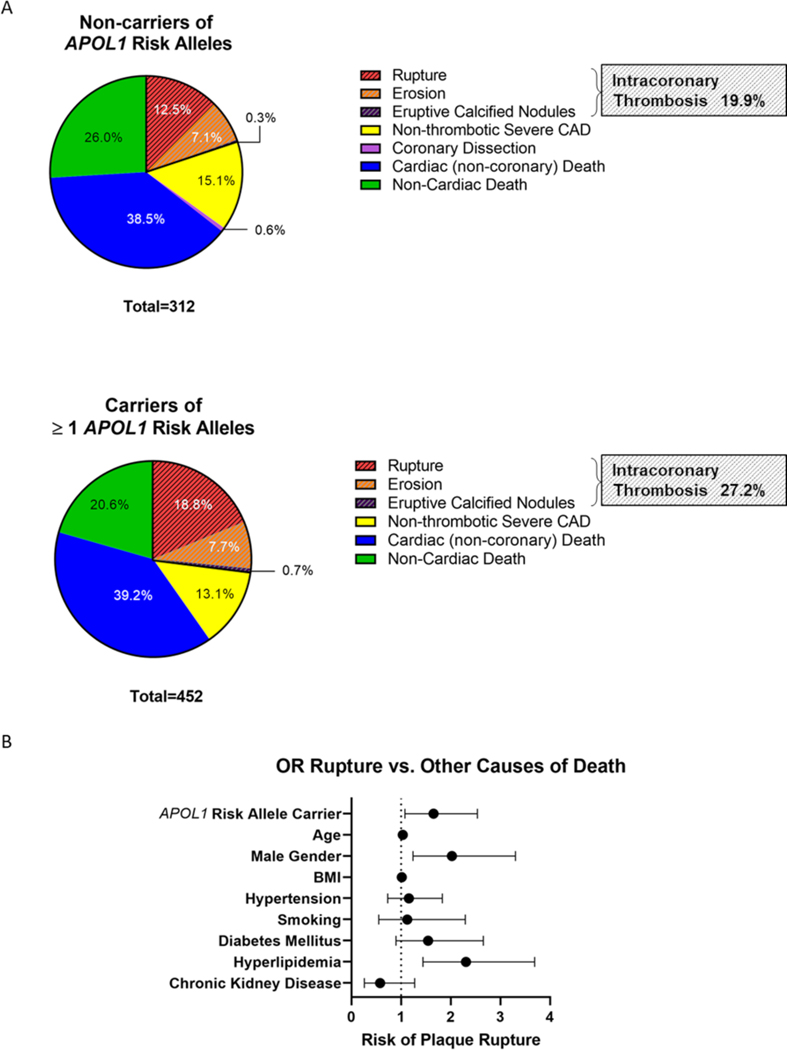
Figure 2. APOL1 Risk Allele Carrier Status and Cause of Death.
A) Intracoronary thrombosis was evident in 19.9% of carriers of the reference alleles, compared to 27.2% of carriers of at least one APOL1 risk allele (p=0.0199). This difference was mostly driven by an increased likelihood of plaque rupture in carriers versus non-carriers of APOL1 risk variants (18.8% vs. 12.5%, p=0.0202). B) APOL1 risk allele carrier status significantly increased the risk for plaque rupture compared with any other causes of death (OR 1.655, 95% CI 1.079–2.539; adjusted p=0.021) in a logistic regression analysis with adjustment for age, sex, BMI, hypertension, smoking, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and CKD.