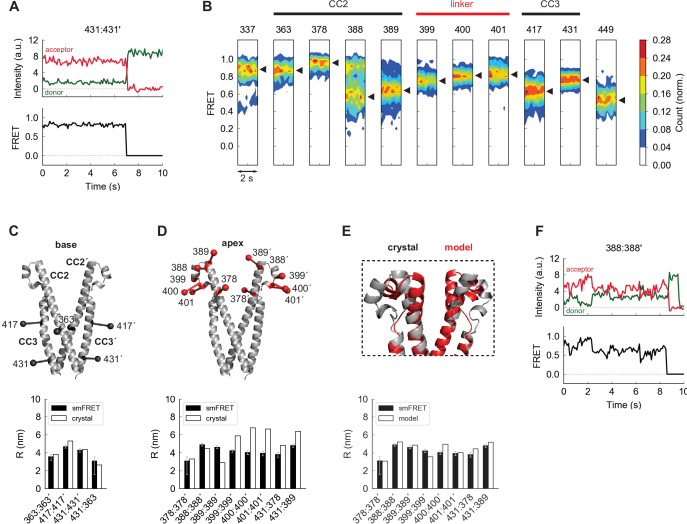
Figure 2. The apex of CAD in ctSTIM1 deviates from the CAD crystal structure.
(A) Representative smFRET recording at the base of CAD (431:431´) showing stable, high FRET. (B) Ensemble density plots of the initial 2 s of inter-subunit smFRET recordings for sites throughout CAD. Predominant FRET levels are shown by arrowheads to the right of each plot. (C–D) Comparison of inter-fluorophore distances from smFRET and the CAD crystal structure. Simulated fluorophores are represented by the average position of a central atom, indicated here as ball-on-stick models (see Materials and methods). For sites near the dimer interface (the 'base' of CAD, C), the smFRET-derived distances (black bars) agree closely with the crystal structure (white bars). Measurements in the apex (D) deviate from the crystal structure. (E) Modified structure (red) generated by a smFRET-constrained optimization of the crystal structure (gray). Outward rotation of the distal CC2 region (aa 379–391) around G379 as a pivot point restored close correspondence between smFRET-derived distances and the crystal structure (bottom). (F) Representative example of smFRET fluctuations in the CAD apex (388:388´).