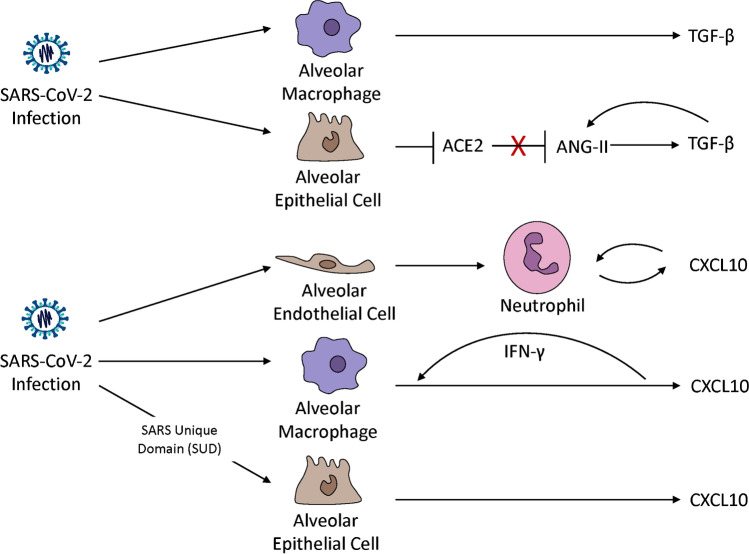
Fig. 1.
CXCL10 and TGF-β are upregulated by SARS-CoV-2 and ARDS in multiple cell types in the lung. SARS-CoV-2 infection upregulates TGF-β in alveolar macrophages and alveolar epithelial cells [33, 34, 121]. SARS-CoV-2 negates the protective role of ACE2 which occurs through negative regulation of ANG-II. ANG-II engages in an autocrine feedback loop to stimulate TGF-β production [30, 31]. Pulmonary endothelial cells recruit neutrophils which increases neutrophil oxidative burst and chemotaxis in a CXCL10-CXCR3 autocrine loop mechanism in viral and non-viral induced lung injury [87•]. SARS-CoV-2-infected macrophages significantly increase the transcription of CXCL10 [121]. CXCL10 increases IFN-γ production [88•] which, in turn, increases CXCL10 in macrophages [90]. The SARS-CoV unique domain (SUD) significantly upregulates the expression of CXCL10 in human lung epithelial cells [86•]