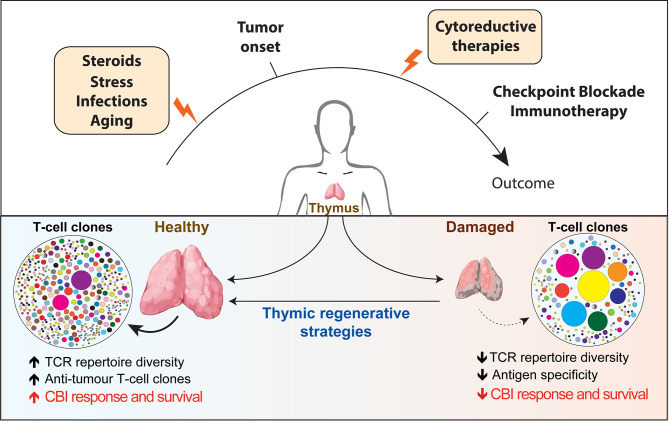
Figure 1.
Overview of the factors affecting thymic function and their potential role in regulating patients’ response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Thymus is particularly sensitive to negative insults that can come from infections, stress, cytoreductive therapies and the physiological process of aging (yellow boxes). The reduction in thymic functionality and in the TCR diversity impaired immune surveillance and may provide a supportive environment for tumors to elude T-cell-mediated response. Instead, a broader TCR repertoire in patients receiving CBI would increase the chance of tumor antigen recognition and favorable long-term clinical outcome. The use of regenerative factors aimed to boost thymic function could improve TCR repertoire diversity and have the potential to significantly extend the clinical efficacy of CBI. TCR, T cell repertoire; CBI, checkpoint blockade immunotherapy; SSA, sex steroids ablation.