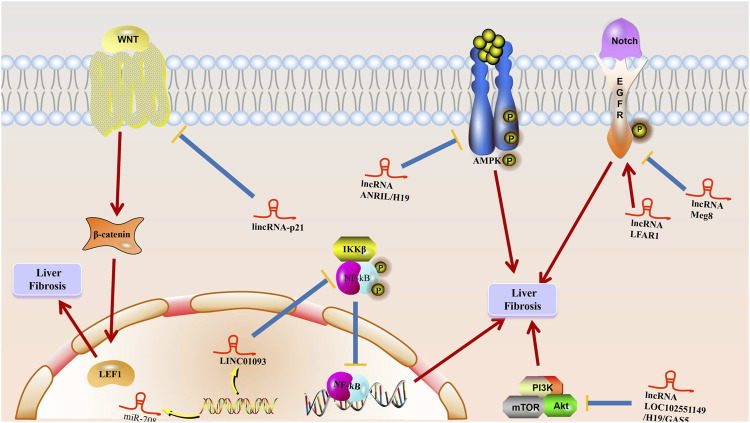
FIGURE 4.
The mechanism of lncRNA to liver fibrosis. Multiple stimuli such as chronic hepatitis B (CHB) damage hepatocytes to initiate wound healing responses, and LncRNAs play a role in promoting activation and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells and inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) at multiple stages, leading to excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins in hepatocytes, resulting in liver fibrosis generation and progression.