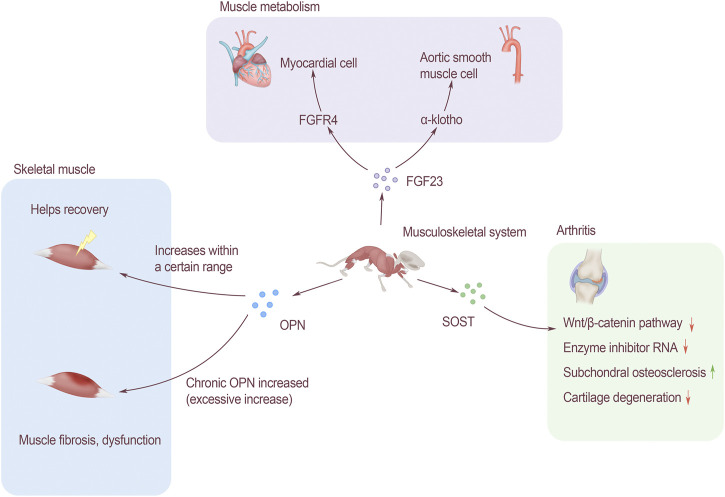
FIGURE 2.
The effect of bone-derived factors on modules of musculoskeletal system. FGF23 affects muscle metabolism. It is associated with cardiomyocytes through FGFR4 and acts on α-Klotho to change aortic smooth muscle. OPN affects skeletal muscles, and the increase in a certain range after injury will help recovery, but long-term increase of OPN will lead to muscle fibrosis and affect muscle function. SOST affects arthritis through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which can inhibit the activity of enzyme inhibitor RNA, promote subchondral bone sclerosis, and inhibit cartilage degradation.