Figure 10.
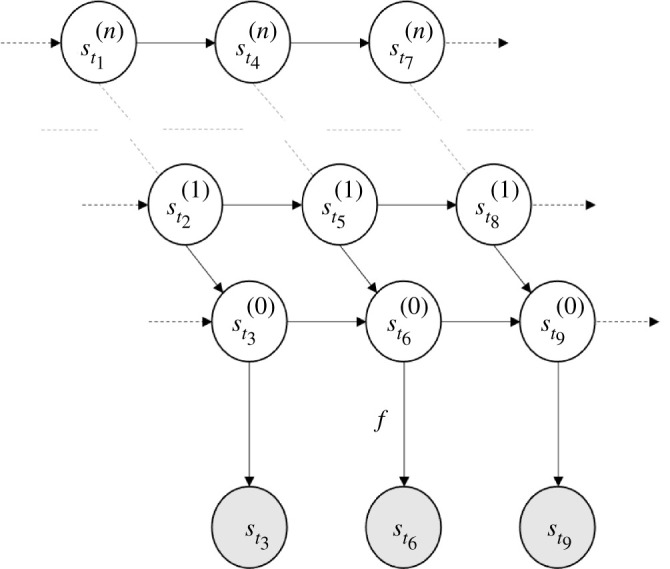
Continuous-time Hidden Markov model. This figure depicts (4.3) in a graphical format, as a Bayesian network [3,31]. The encircled variables are random variables—the processes indexed at an arbitrary sequence of subsequent times . The arrows represent relationships of causality. In this hidden Markov model, the (hidden) state process is given by an integrator chain—i.e. nested stochastic differential equations . These processes , can, respectively, be seen as encoding the position, velocity, jerk etc, of the process .
