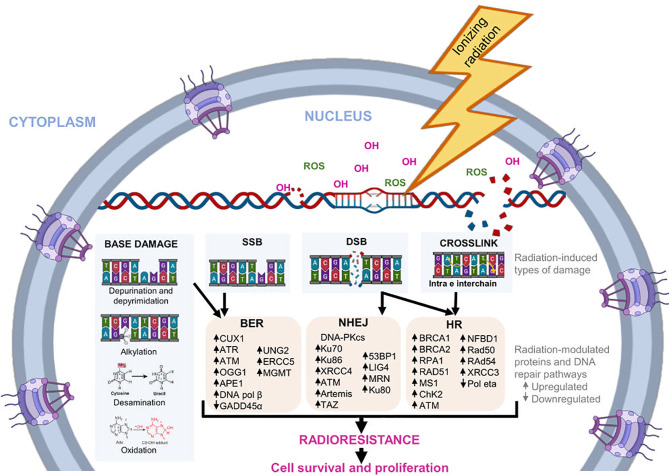
Figure 1.
DNA repair pathways induced by radiation. During radiotherapy, IR can alter the chemical structure of DNA directly or indirectly. Indirectly, it promotes the formation of molecules, such as the OH- ion and ROS, which bind to nucleotides and modify them structurally. The main modifications induced by radiation are base damage, crosslink, SSB, and DSB. In response, cells regulate the expression of several genes and proteins involved in different DNA repair pathways, such as BER, NHEJ, and HR. The activation of this pathways helps to reduce radiation-induced DNA damage, favoring the survival and proliferation of tumor cells, as well as cellular radioresistance.