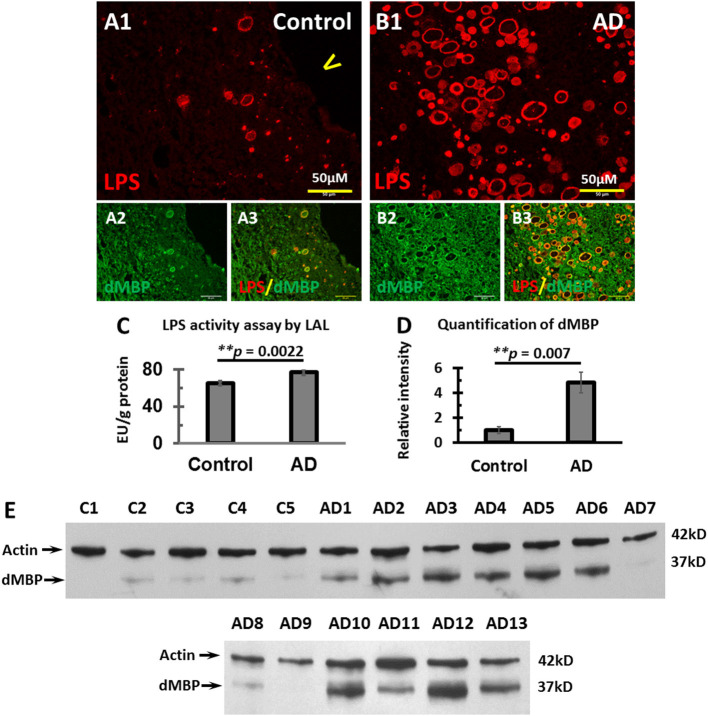
Figure 5.
Colocalization of LPS with dMBP, LPS LAL assay, and Western blot analysis of dMBP in the PVWM of AD and control brains. (A) LPS (A1) and dMBP (A2) in control PVWM were colocalized (A3). (B) LPS (B1) and dMBP (B2) in AD PVWM were colocalized (B3). (C) The LAL assay for LPS of PVWM showed significantly greater LPS activity in AD (77.3 ± 3.1 EU/g, n = 12) compared to controls (65 ± 2.1 EU/g, n = 10, p = 0.0022). (D) The dMBP band intensity in PVWM was greater in AD (4.8 ± 0.8, n = 13) compared to controls (1 ± 0.3, n = 5, p = 0.007). (E) Western blots of PVWM for dMBP and β-actin for 5 controls (C1-C5) and 13 AD samples (AD1-AD13). β-actin was used as a loading control. Note: LAL, Limulus Amoebocyte Lysate assay for LPS; dMBP, degraded myelin basic protein; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; AD, Alzheimer's disease; Bar = 50 μm.