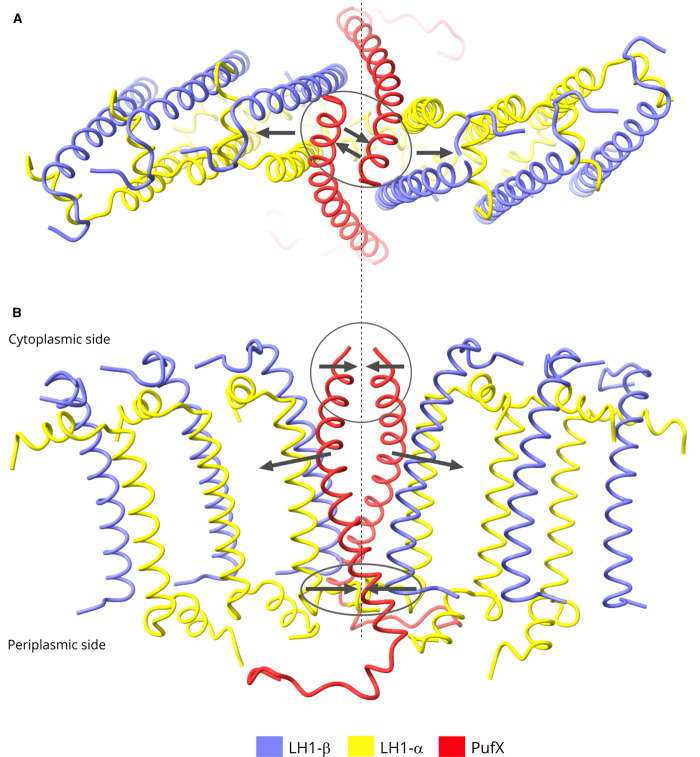
Figure 5. The role of PufX in imposing a bent conformation on the RC-LH1 dimer complex.
Pigments and lipids, as well as most of the LH1 subunits and the RC, have been omitted for clarity. (A) Top view, from the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. The arrows within the ellipse illustrate the attractive interactions between N-terminal regions of opposing PufX polypeptides, which help to bind the two halves of the dimer together. The diverging arrows represent the effects of each PufX as it lies diagonally across its adjacent LH1αβ subunit, pushing them apart. (B) As in (A) but viewed in the plane of the membrane, with the N-terminal PufX interactions within the circle, and multiple attractive interactions near the periplasmic face, within the ellipse, that hold the bottom halves of the complex tightly together. As in (A) the diverging arrows represent the central LH1αβ subunits being pushed apart by the PufX transmembrane regions.