FIG. 3.
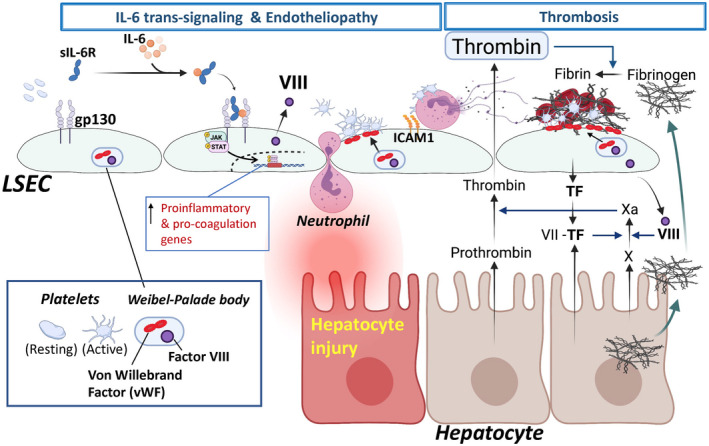
Liver sinusoidal endotheliopathy and liver injury in COVID‐19. IL‐6 trans‐signaling and endotheliopathy: IL‐6 is highly elevated in patients with COVID‐19 and is related to liver injury. LSECs are not thought to express the membrane‐bound ligand‐binding domain for IL‐6. However, the complex of IL‐6 and sIL‐6R binds to gp130 on the cell membrane, inducing IL‐6/JAK/STAT signaling, known as IL‐6 trans‐signaling. The IL‐6 trans‐signaling induces liver sinusoidal endotheliopathy with neutrophil infiltration and a hypercoagulable LSEC phenotype. IL‐6 trans‐signaling increases expression of proinflammatory (ICAM1, CXCL1, CXCL2, P‐selectin, and E‐selectin) and procoagulation genes (factor VIII and vWF). Weibel‐Palade body includes vWF and factor VIII in LSECs. IL‐6 trans‐signaling promotes movement of vWF to the LSEC surface, facilitating platelet attachment, an initial step of the thrombus formation. Endotheliopathy is associated with neutrophil recruitment, potentially leading to hepatocyte injury. Platelet–neutrophil interactions mediate NET formation. Microvascular thrombosis: Thrombus (blood clots) consists of accumulated platelets (platelet plug) and a mesh of cross‐linked fibrin. Thrombosis involves interplay among various cell types and cascades of coagulation factors. Platelet adhesion to the injured LSECs is an early step in thrombosis. Attached platelets are activated by the action of thrombin (also known as activated factor II), which facilitates additional recruitment of circulating platelets to the injury site to form a platelet plug. Thrombin is generated from prothrombin by a series of well‐described cascades of coagulation factors. Damaged endothelial cells and hepatocytes produce a procoagulant molecule, TF, which binds and activates circulating procoagulant molecule factor VII. Activated factor VII proteolytically cleaves factor X to form Xa, which then converts prothrombin to its active form, thrombin. In addition to platelet activation and aggregation, thrombin facilitates a cascade of coagulation events to generate fibrin and cross‐links fibrin chains to form a large fibrin mesh. Patients with COVID‐19 show an elevated fibrinogen level. Abbreviations: CXCL, chemokine (C‐X‐C motif) ligand 1; NET, neutrophil extracellular trap; TF, tissue factor; Xa, active factor X.
