TABLE 5.
Relationship between pathogenic mechanisms and clinical outcomes in severe/critical COVID‐19
| Evolving endotypes a | Phenotypes |
|---|---|

|
1. Sepsis‐like Syndrome 44 , 45 , 116 , 117 |

|
2. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation 49 , 51 , 108 , 117 |
|
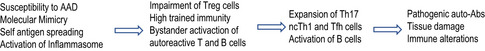
3. MIS‐C and Autoimmune‐ Auto‐inflammatory –like syndrome. 44 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 114 |

|
4. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome 11 , 107 , 112 , 118 , 123 , 124 |

|
5. Cytokine Release Syndrome 13 , 14 , 107 , 113 |

|
6 SecondaryHaemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis 107 , 115 |

|
7. Macrophage Activating Syndrome 107 , 112 , 117 , 123 |

|
8. Multiorgan Failure 48 , 104 , 110 , 111 , 117 |
Abbreviations: AAD: Auto‐inflammatory/autoimmune Disorders; Abs, antibodies; C’, complement; MBL, membrane binding proteins; MDSC, Myeloid‐derived suppressive cells; ncTh1, not classical Th1 cells; NETs, neutrophil extracellular traps; NK, Natural killer cells; pDC, plasmocitoid Dendritic cells; TF, tissue factor; Tfh, Follicular T helper cells; TLRs, Toll‐like receptors; vWF, von Willebrand factor.
Each pathway should not be considered one way, since conditions favoring multiple mechanisms can coexist or intersect each other. Evolving endotypes leading to Phenotypes 1, 2, 5, 6 needs further investigation.and, at presenr, must be considered hypothetical.
