FIGURE 1.
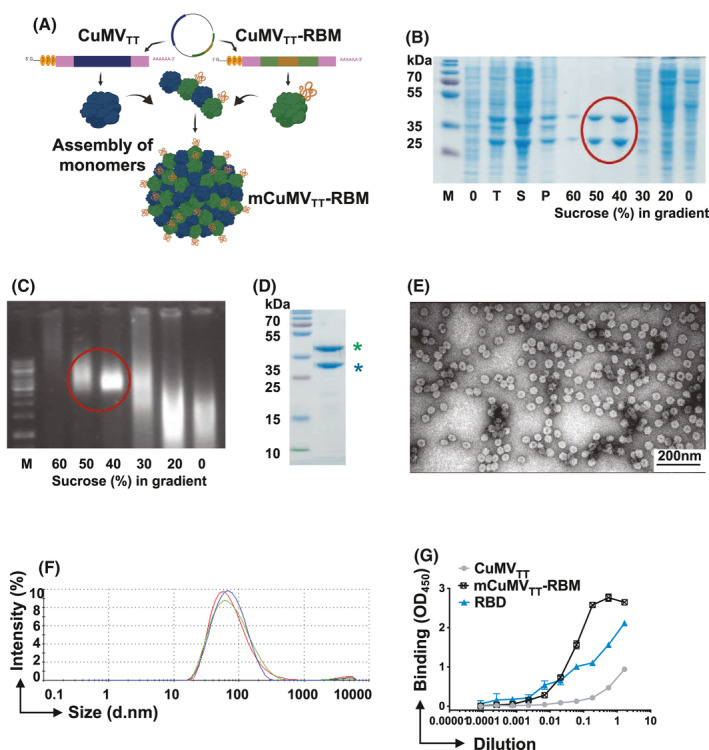
CuMVTT‐VLPs constitute an efficient platform for genetically fusing the receptor‐binding motif (RBM). A, Schematic depiction of E. coli cells containing pETDuet‐1‐derived plasmid, allowing the coexpression of CuMVTT‐RBM fusion and unmodified CMVTT genes and production of mosaic VLPs termed (mCuMVTT‐RBM), B, SDS‐PAGE analysis of the production and sucrose gradient purification of mCuMVTT‐RBM. M—protein size marker (Thermo Scientific), 0 – total proteins in E.coli C2566 cells before IPTG induction; T—total proteins in E.coli C2566 cells after IPTG induction and 18h cultivation at 20℃; S—soluble proteins in E.coli C2566 cells after induction and 18 h cultivation; P—insoluble proteins in E.coli C2566 cells after induction and cultivation; 60 – 0 – sucrose gradient fractions after separation of cell lysate in Beckman SW32 rotor; mCuMVTT‐RBM VLP containing sucrose fractions are labeled with red circle; C, native agarose gel analysis of the sucrose gradient fractions after sucrose gradient purification of mCuMVTT‐RBM. M—DNA size marker (Thermo Scientific), 60–0– sucrose gradient fractions after separation of the cell lysate in Beckman SW32 rotor; mCuMVTT‐RBM VLP containing sucrose fractions are labeled with red circle; D, SDS‐PAGE analysis of purified mCuMVTT‐RBM VLPs. M—protein size marker (Thermo Scientific), asterisk (blue) refers to unmodified CuMVTT monomer and asterisk (green) refers to genetically modified CuMVTT‐RBM E, Electron microscopy analysis of purified mCuMVTT‐RBM VLPs; F, DLS analysis of purified mCuMVTT‐RBM VLPs. G, ACE2 binding to mCuMVTT‐RBD vaccine candidate, CuMVTT, and RBD alone were used as controls. Plates coated with 1µg/ml of ACE2. Binding was revealed using anti‐CuMV mAb. One representative of 2 similar experiments is shown
