FIGURE 4.
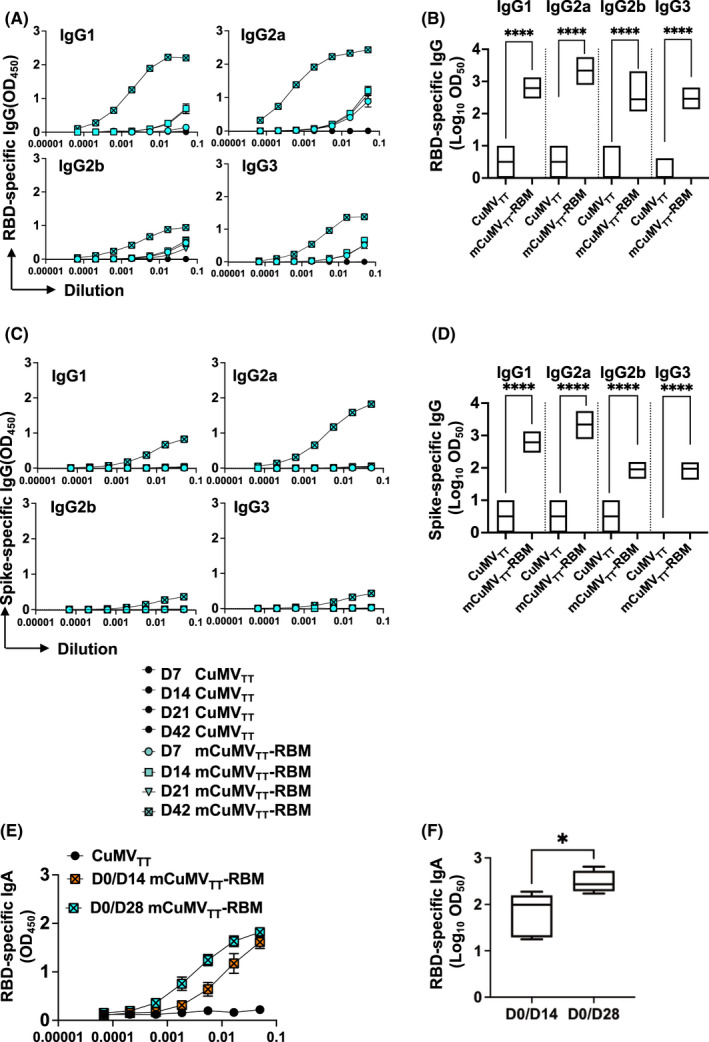
mCuMVTT‐RBM promotes IgA production and IgG responses are dominated with IgG2a subclass. A, RBD‐specific IgG titer for the groups vaccinated with CuMVTT as a control or mCuMVTT‐RBM on days 7, 14, 21, and 42 measured by ELISA OD450. B, Log10OD50 of RBD‐specific IgG titers for the groups vaccinated with CuMVTT or mCuMVTT‐RBM on days 7, 14, 21 and 42 (Data from A). C, spike‐specific IgG titers for the groups vaccinated with CuMVTT or mCuMVTT‐RBM on days 7, 14, 21, and 42 measured by ELISA OD450. D, Log10OD50 of spike‐specific IgG titers for the groups vaccinated with CuMVTT or mCuMVTT‐RBM on days 7, 14, 21, and 42 (Data from C). CuMVTT n=5 and mCuMVTT‐RBM n=10. E, RBD‐specific IgA titer for the groups vaccinated with CuMVTT or mCuMVTT‐RBM using D0/D14 or D0/D28 regimens, measured by ELISA OD450. F, Log10OD50 of RBD‐specific IgA titer for the groups vaccinated with CuMVTT or mCuMVTT‐RBM using D0/D14 or D0/D28 regimens, sera of day 35 was used. CuMVTT n=5 and mCuMVTT‐RBM n=5. Statistical analysis (mean ±SEM) using one‐way ANOVA in B and D or Student's t test in F. One representative of 3 similar experiments is shown. The value of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant (*p<0.01, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0001)
