FIG 4.
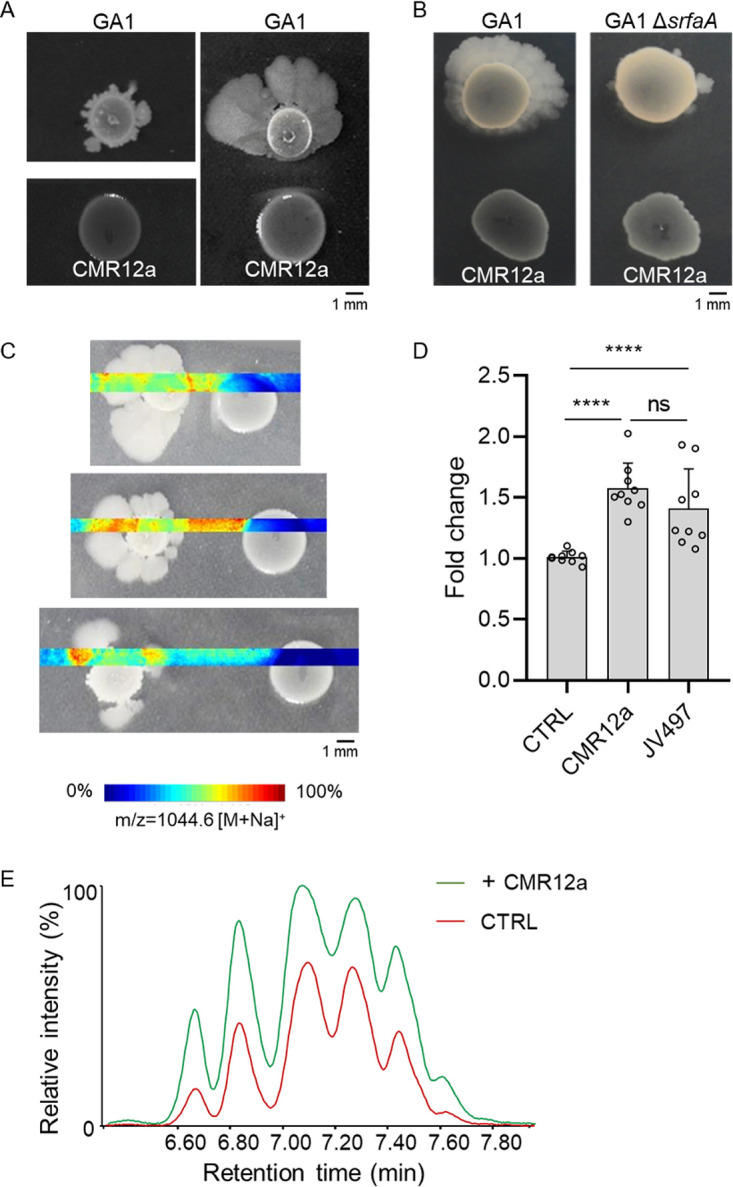
Distance- and surfactin-dependent enhanced motility of B. velezensis GA1 mediated by interaction with Pseudomonas. (A) GA1 motility phenotype on EM jellified medium when cultured alone (left) or in confrontation with CMR12a (1 mm) (right). (B) Motility pattern of GA1 or the ΔsrfaA surfactin-deficient mutant in confrontation with CMR12a (5 mm). (C) MALDI FT-ICR mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) heat maps showing spatial localization and relative abundance of ions corresponding to the C14 surfactin homolog (most abundant) when GA1 is confronted with CMR12a at increasing distances. (D) Comparison of surfactin production (expressed in fold change) in GA1 culture supplemented with 4% (vol/vol) of CMR12a or JV497 supernatants. The unsupplemented culture was fixed at 1 (CTRL). Bars show mean ± SD (n = 9). Statistical comparisons between treatments were assessed with the Mann-Whitney test; ns, not significant; ****, P < 0.0001. (E) UPLC-MS extracted ion chromatogram (EIC) illustrating the relative abundance of surfactin produced in GA1 EM medium when cultured alone (CTRL in red) or supplemented with 4% (vol/vol) CMR12a (+CMR12a in green). The different peaks correspond to the structural variants differing in fatty acid chain length.
