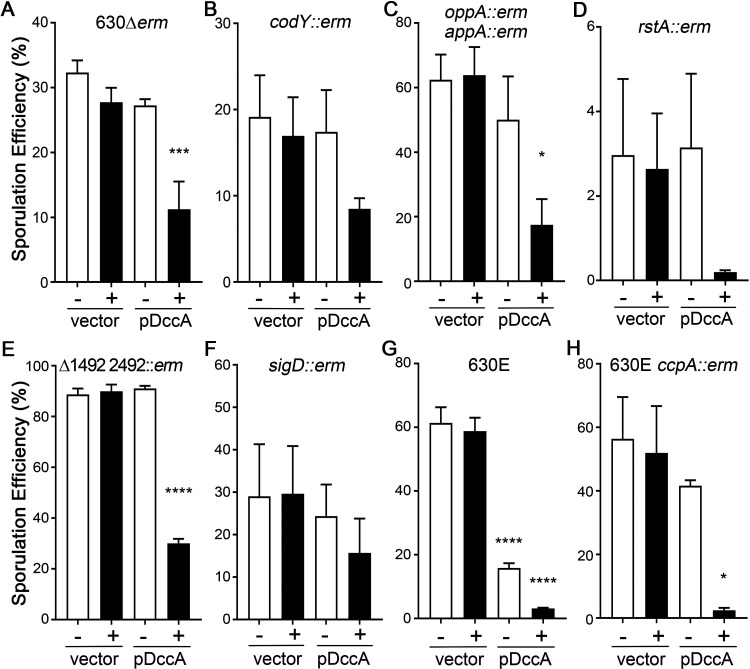
FIG 6.
c-di-GMP does not inhibit sporulation through known sporulation factors. Shown are data from ethanol-resistant sporulation assays of 630Δerm pMC211 (RT762) and 630Δerm pDccA (RT763) (A), 630Δerm codY::erm pMC211 (MC947) and 630Δerm codY::erm pDccA (MC948) (B), 630Δerm oppB::erm appA::erm pMC211 (MC924) and 630Δerm oppB::erm appA::erm pDccA (MC925) (C), 630Δerm rstA::erm pMC211 (MC926) and 630Δerm rstA::erm pDccA (MC927) (D), 630Δerm ΔCD1492 CD2492::erm pMC211 (MC928) and 630Δerm ΔCD1492 CD2492::erm pDccA (MC929) (E), 630Δerm sigD::erm pMC211 (MC864) and 630Δerm sigD::erm pDccA (MC865) (F), 630E pMC211 (MC943) and 630E pDccA (MC944) (G), and 630E ccpA::erm pMC211 (MC945) and 630E ccpA::erm pDccA (MC946) (H) grown on 70:30 sporulation agar supplemented with 2 μg/ml thiamphenicol in the absence or presence of 0.5 μg/ml nisin, as indicated, at H24. The means and standard errors of the means from at least three biological replicates are shown. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001 (by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s posttest comparing values to those of the respective parent strains with an uninduced vector). Note that the y axes for each panel vary depending on the sporulation frequency of the strain tested.