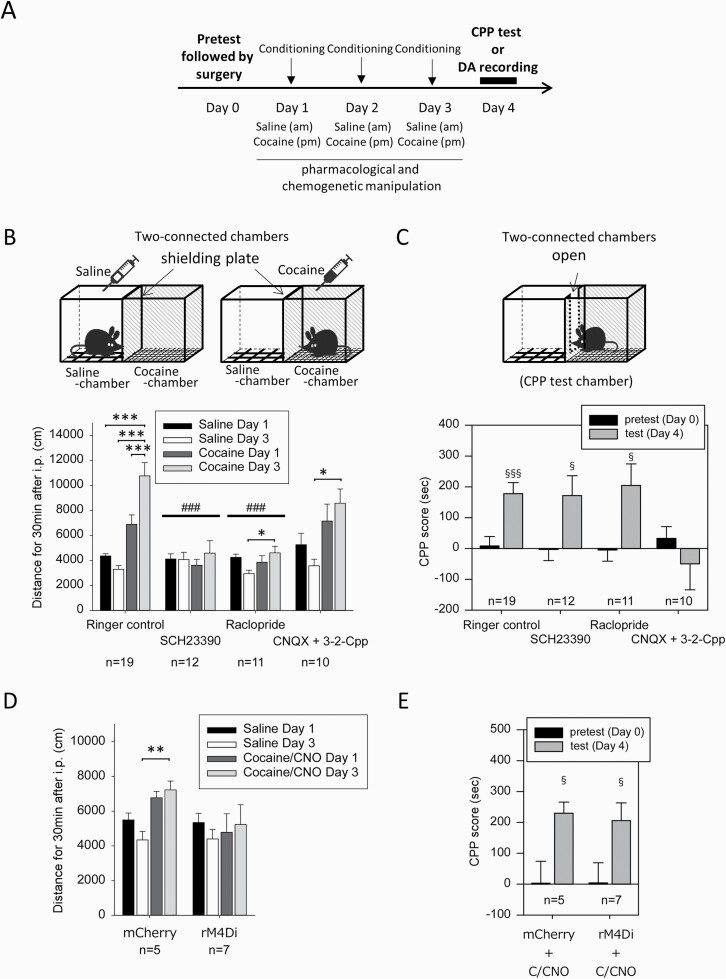
Figure 2.
Effects of antagonist infusion into the prefrontal cortex (PFC) during cocaine conditioning on the locomotor response and conditioned place preference (CPP) to cocaine. (A) Daily injections of saline and cocaine (7.5 mg/kg) for conditioning were conducted as described in Figure 1A. Surgery for microdialysis probe implantation was conducted on day 0 following the pretest of chamber preference. Pharmacological and chemogenetic manipulation was performed during conditioning (day 1–3), and the CPP test was performed on day 4. (B–C) Pharmacological ligands (a D1 receptor antagonist, SCH23390 [10 µM]; a D2 receptor antagonist, raclopride [10 µM]; ionotropic glutamate antagonists, CNQX [10 µM] plus 3-2-Cpp [30 µM]) were infused into the PFC during conditioning (day 1–3). The locomotor response to saline or cocaine injection was evaluated in paired chambers using the 2-connected chamber apparatus with a shielding plate on day 1 and day 3 (B), and cocaine CPP was evaluated using the 2-connected chamber apparatus without a shielding plate on day 4 (C). (D, E) For chemogenetic inhibition of D1 receptor-expressing neurons in the PFC, saline and CNO (1 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered 30 minutes before the saline-paired place conditioning and cocaine-paired place conditioning (day 1–3), respectively, in [Drd1]-Cre mice injected with Gi-DREADD virus (rAAV-hsyn-DIO-rM4D(Gi)-mCherry) or control virus (rAAV2-Ef1a-DIO-mCherry) into the PFC. The locomotor response to saline injection or cocaine injection after CNO administration (C/CNO) was evaluated on day 1 and day 3 (D), and cocaine CPP was evaluated on day 4 (E). Data represent mean ± SEM. The number of mice is indicated under each experimental group. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 as indicated; 1-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. ###P < .001 vs Ringer’s control; mixed effect models. §P < .05, §§§P < .001 vs CPP score in pretest, Welch’s t test.