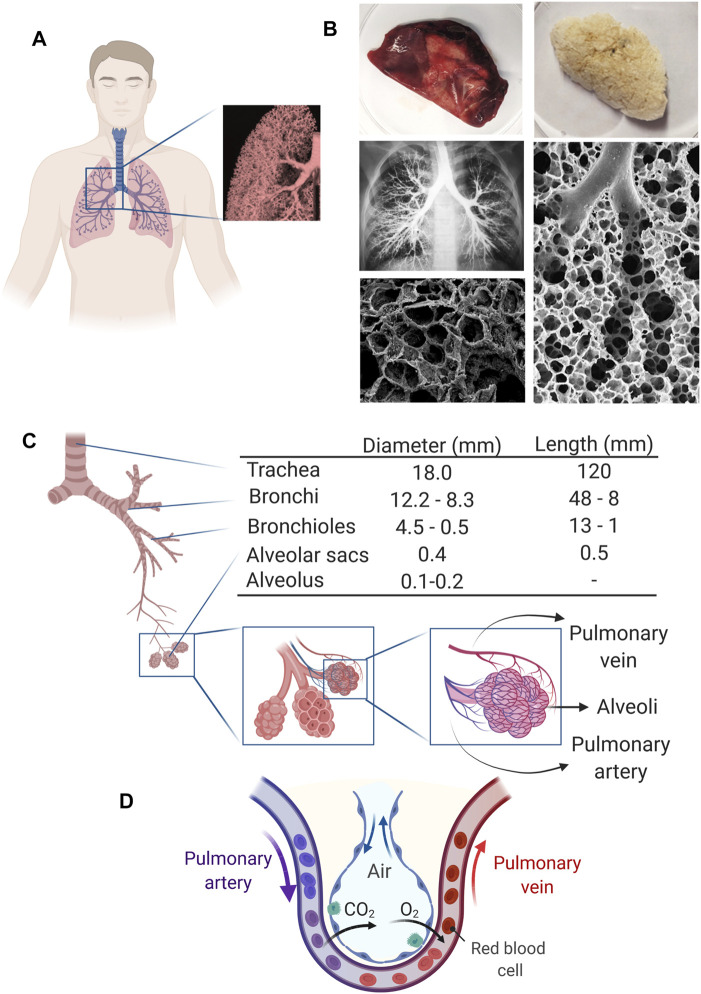
FIGURE 1.
Human lung structure and function. (A) Representation of the lung in the human body and its appearance. Inset: Pulmonary tissue contains many interconnected airways that give the lung its spongy structure. (B) Macroscopic images of native and decellularized human lungs (Reproduced from reference (Booth et al., 2012)) along with images that show the internal structure of lung tissue (Reproduced from references (Freed et al., 2012; Weibel 2013)). (C) Representation of the respiratory tree and the airway branching of the human lung and its approximate dimensions. Dimensions for all structures are reported for the resting lung, while for the alveolus, a range for resting and expanded lung is reported (Data retrieved from references (Bouhuys 1977; Bajaj et al., 2016) and (Ochs and Nyengaard. 2004)). (D) Schematic representation of the gas exchange occurring at the alveolus vascular interface.