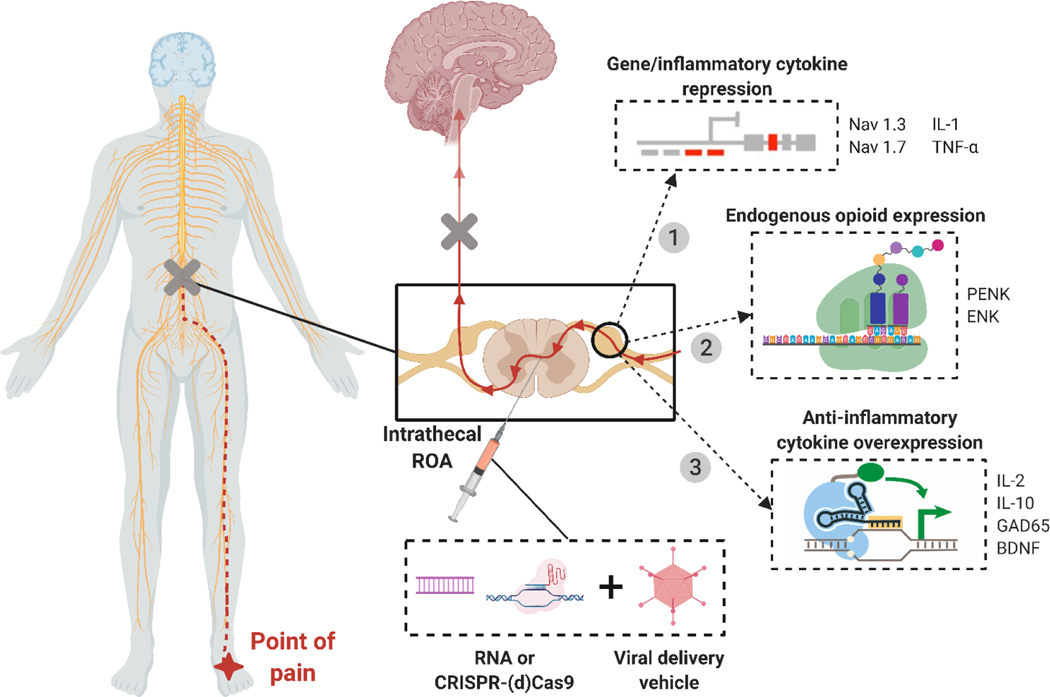
Figure 5. Methods of viral gene therapy for pain treatment.
Schematic showing various methods of gene therapy for pain treatment. 1) Repression of genes (Nav1.3, Nav1.7) or inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, TNF-α) to reduce pain signaling and inflammation in affected areas. 2) Expression of preproenkephalin (PENK) and enkephalin (ENK), which act as endogenous opioids by binding to opioid receptors and mediating pain. 3) Overexpression of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-2, IL-10, GAD65, BDNF) to reduce inflammation, immune response, and inflammatory pain. Adapted from Moreno et al.[195].