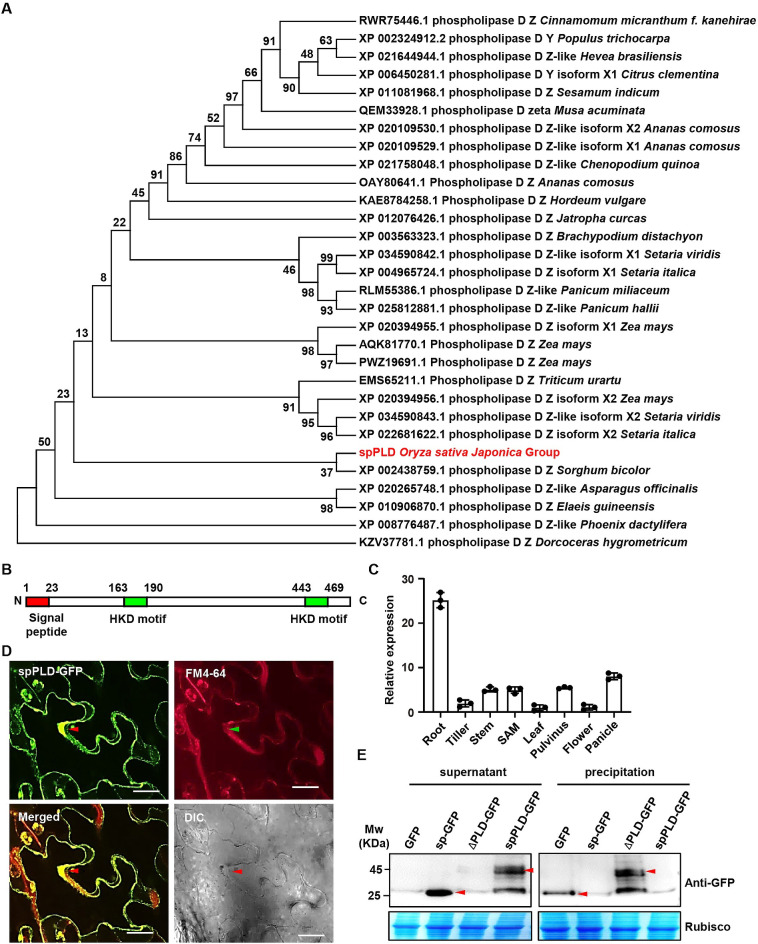
Fig 1. spPLD is a secretory PLD.
A. Sequence alignment was performed with BLAST and the top 30 proteins with protein functional annotation and identity at more than 70% were analyzed. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1000 replicates is generated to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) is shown next to the branches. NCBI accession number, protein ID and species of analyzed protein are shown. B. Protein structural analysis showed the presence of two HKD motifs and one signal peptide (sp) at N-terminus of rice spPLD. C. qPCR analysis revealed the spPLD expression in various tissues including roots, tillers, stems, SAM, leaves, pulvini, flowers and panicles. Expression level was normalized to ACTIN1 transcript and relative expressions were calculated by setting spPLD expression in leaves as 1.0. Experiments were repeated three times and data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). D. Secretion of spPLD was confirmed by observing N. benthamiana plants expressing spPLD-GFP fusion protein. FM4-64 was used to highlight the plasma membrane. Plasmolysis was conducted by 1 M mannitol treatment for 10 min. The secreted sections were highlighted by arrows. DIC, bright field. Scale bar = 50 μm. E. Western Blotting analysis confirms the secretion of spPLD. Various fusion proteins were transiently expressed in rice protoplasts. After incubation for 48 h, proteins of supernatant (incubation medium) and precipitation (protoplast homogenate) were extracted and analyzed by Western Blotting using anti-GFP antibody. Arrows highlighted the GFP (sp-GFP) and spPLD-GFP (ΔPLD-GFP) proteins.