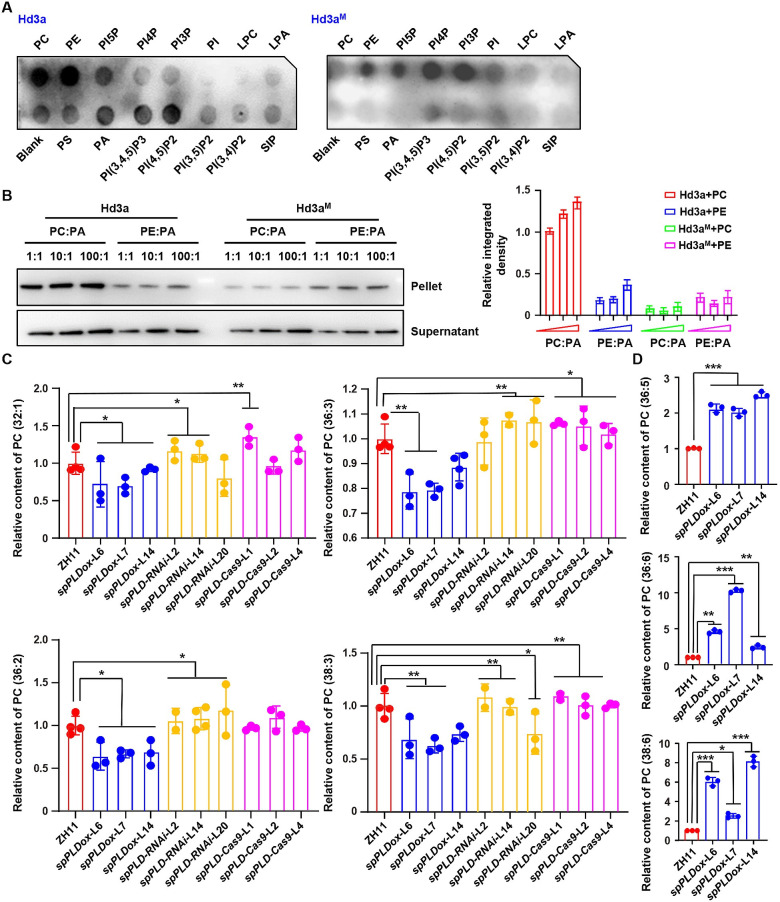
Fig 3. Altered PC species under spPLD overexpression or deficiency.
A. Fat-western immunoblot analysis revealed the binding of rice Hd3a (left) and Hd3a with mutated PC binding sites (Hd3aM, right) to phospholipids. The phospholipid type of each dot is indicated. PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PS, phosphatidylserine; PA, phosphatidic acid; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; S1P, sphingosine 1-phosphate; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PI3P, PI 3-monophosphate; PI4P; PI5P; PI(3,4)P2, PI 3,4-bisphosphate; PI(3,5)P2; PI(4,5)P2; PI(3,4,5)P3, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. B. Liposome binding assay (left) and quantitative analysis (right) confirmed the preferential binding of Hd3a to PC. His-tag fused Hd3a and Hd3a with mutated PC binding sites (Hd3aM) were purified and incubated with liposomes containing different PC:PA or PE:PA ratios. After collecting the liposomes, the portion of proteins bound to liposomes was detected by western blotting using anti-His antibody. Nonbinding protein was detected in the supernatant (bottom). Band density is measured by Image J and relative density was calculated by setting the intensity under PC:PA ratio 1:1 as 1.0. Data were presented as means ± SD (n = 3, right). C-D. Relative content of predominant PCs with different saturation status, PC (32:1), PC (36:2), PC (36:3) and PC (38:3) (C); PC (36:5), PC (36:6) and PC (38:6) (D), in ZH11 and various lines with altered spPLD expressions. Ten rice shoot apical meristem before bolting were collected and used for lipids extraction. Phospholipids were profiled by a lipidomic approach using mass spectrometry. Experiments were biologically repeated three times and data were shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed by Tukey’s test (*, p <0.05; **, p < 0.01 ***, p < 0.001, compared to ZH11).