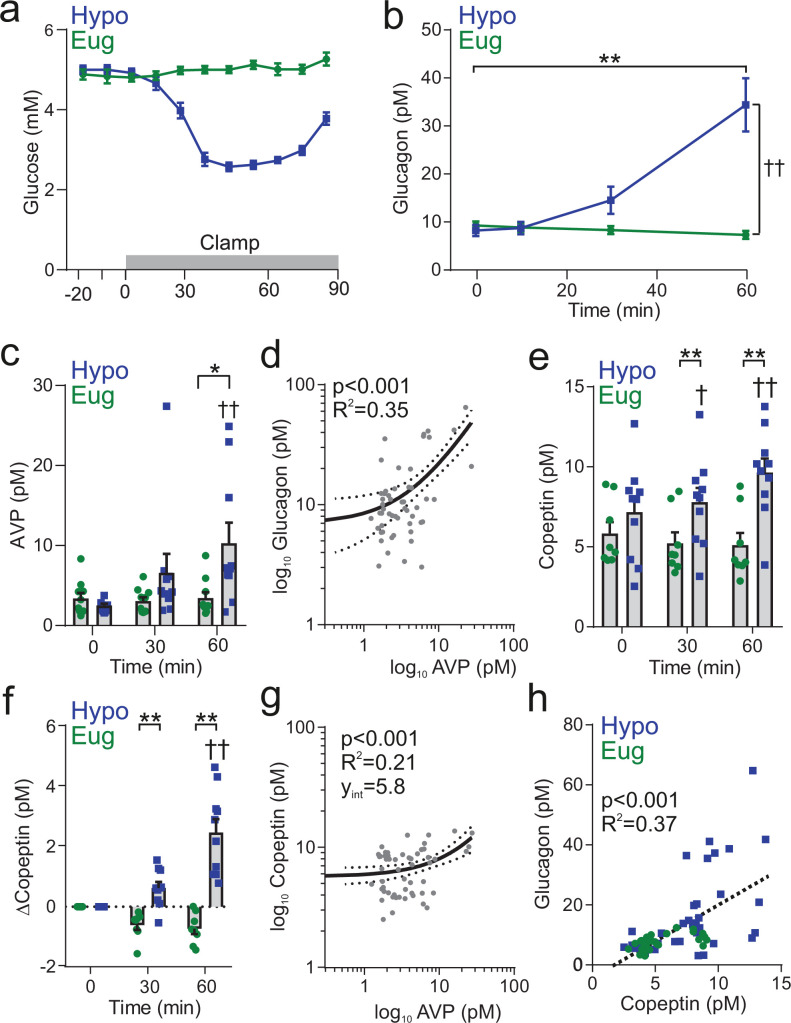
Figure 6. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia evokes copeptin and glucagon secretion in human participants.
(a) Blood glucose was clamped at euglycemia (Eug) and followed during insulin-induced hypoglycemia (Hypo). n=10 healthy human subjects. The clamp was initiated at time 0 min and terminated at 60 min. (b) Plasma glucagon measurement during insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Time point versus 0 min; p<0.01=**. Between treatments; p<0.01=††. (c) Plasma AVP measurement during and following clamping period. Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Hypoglycemia 0 min versus 60 min; p<0.01=††. Hypoglycemia 0 min versus 30 min; p=0.07. Between treatments; p<0.05=*. (d) Log-log plot of plasma AVP and plasma glucagon. Data points are 0, 30, and 60 min during hypoglycemic clamp. Linear regression (solid line) with 95% CI (dashed line). (e) Plasma copeptin measurement during hypoglycemic or euglycemic clamp. Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Indicated time point versus 0 min; p<0.05=†, p<0.01=††. For hypoglycemic clamp 0 min versus 30 min, p=0.07. Between treatments; p<0.01=**. (f) Change in plasma copeptin from baseline (time=0 min). Two-way RM ANOVA by both factors. Indicated time point versus 0 min; p<0.01=††. For hypoglycemic clamp 0 min versus 30 min, p=0.07. Between treatments; p<0.01=**. (g) Log-log plot of plasma AVP and plasma copeptin (as plotted in Roussel et al., 2014). Data points are 0, 30, and 60 min during hypoglycemic clamp. Linear regression (solid line) with 95% CI (dashed line). (h) Correlation of change in copeptin and glucagon, with a linear regression (dashed line). Data points are from both euglycemia and hypoglycemia at 0, 10, 30, and 60 min.