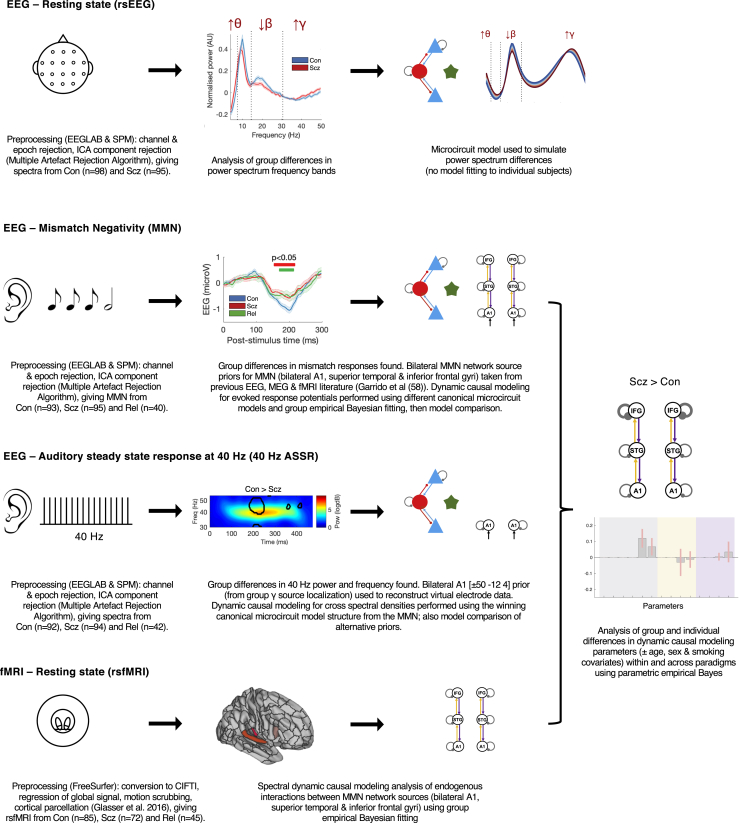
Figure 1.
An overview of the analysis. This schematic illustrates the key steps in the preprocessing of the electroencephalography (EEG) (resting state [rs], mismatch negativity [MMN], and 40-Hz auditory steady-state response [ASSR]) and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rsfMRI) paradigms and their subsequent analysis using dynamic causal modeling (DCM) and parametric empirical Bayes. Simplified depictions of the paradigms are shown in the first column (see the Supplement for details), with group differences in EEG data features in the second column (first 3 rows) and DCM in the third column. The EEG data control group (Con) versus people with schizophrenia diagnoses (PScz) group differences are (from first to third rows) in rsEEG θ, β, and γ frequency band power (Figure 2A), MMN responses (Figure 3A), and 40-Hz ASSR power (Figure 4C). The second column of the final row (rsfMRI) shows the Glasser parcellation areas primary auditory cortex (A1) (middle), A4 (left), and 44 (right) containing the MMN sources A1, superior temporal gyrus (STG), and inferior frontal gyrus (IFG), respectively; these were used as nodes in the rsfMRI analysis, so that results could be compared across data modalities. Key preprocessing and analysis steps are described below the illustrations. DCM for EEG uses a cortical microcircuit model, shown on the left in the third column (also see Figure 2C). It contains superficial and deep pyramidal cells (blue triangles), inhibitory interneurons (red circles), and spiny stellate cells (green stars). The lower three DCM illustrations include macroscopic model structures, i.e., the cortical areas involved: A1, STG, and IFG (58). In the rsEEG analysis (top row), a single-area DCM was used to reproduce power spectra characteristic of each group. In the remaining paradigms, models were fitted to the data and parametric empirical Bayes was used to analyze group and individual differences. The final column depicts an example analysis (from Figure 3F) of group differences in DCM parameters between Con and PScz in the MMN. ICA, independent component analysis; MEG, magnetoencephalography; Rel, first-degree relative.