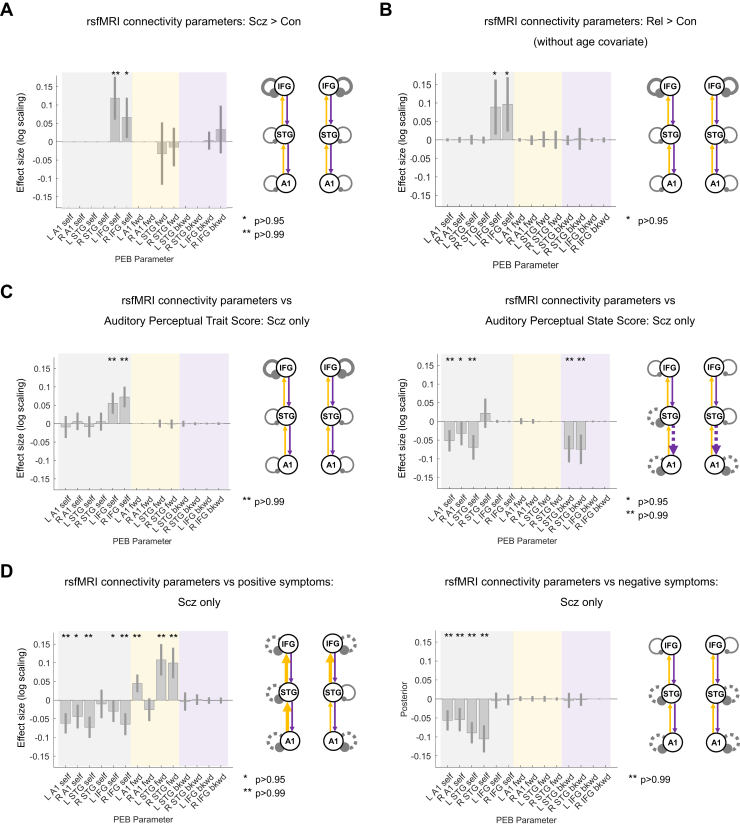
Figure 5.
Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rsfMRI) modeling analysis. (A) For comparative purposes, the rsfMRI connectivity analysis was conducted on the same network as the mismatch negativity (MMN) analysis. Results for control subjects (Con) (n = 85) and people with schizophrenia diagnoses (PScz) (n = 72) are shown in the same format as Figure 3F. As in the MMN, PScz showed increased self-inhibition in the bilateral inferior frontal gyrus (IFG). Inclusion of chlorpromazine equivalent dose as a covariate still showed increased self-inhibition in left (L) IFG but only at p > .75. (B) rsfMRI connectivity analysis without covariates for Con (n = 85) and first-degree relatives (Rel) (n = 45) is shown. Similar to PScz, Rel show increased self-inhibition in the bilateral IFG, but this effect disappeared with addition of the age covariate (p < .75). (C) Left: within PScz, abnormal auditory percepts (trait measure) related to increased self-inhibition in the bilateral IFG. Right: conversely, abnormal auditory percepts (state score, i.e., experiences within the last week only) relate to disinhibition in temporal areas and also a loss of top-down connections within the auditory cortex. The right (R) primary auditory cortex (A1) effect was attenuated if age, sex, and smoking covariates were not included and if a chlorpromazine dose equivalent covariate was added. (D) Left: within PScz, Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale positive symptom score related to disinhibition throughout the MMN network and increased forward (fwd) connectivity in 3 of 4 connections. Most effects were robust to addition of chlorpromazine dose equivalents as a covariate (all p > .99 except L IFG self-inhibition, p > .75), removal of the hallucinations score from the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale positive symptom total (all p > .95 except L IFG and R A1 self-inhibition, p > .75), and analysis without covariates (all p > .99 except L IFG self-inhibition, p > .75). Right: within PScz, Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale negative symptom score related to disinhibition in temporal nodes of the MMN network. All effects shown (except Rel > Con) are also present without the addition of age, sex, and smoking covariates and if participants (2 Con, 8 PScz) with rsfMRI signal-to-noise ratio <25 are excluded (all p > .95). Some rsfMRI results are no longer significant without global signal regression (Figure S7). No results change substantially with inclusion of chlorpromazine dose equivalent as a covariate unless stated. bkwd, backward; PEB, parametric empirical Bayes; STG, superior temporal gyrus.