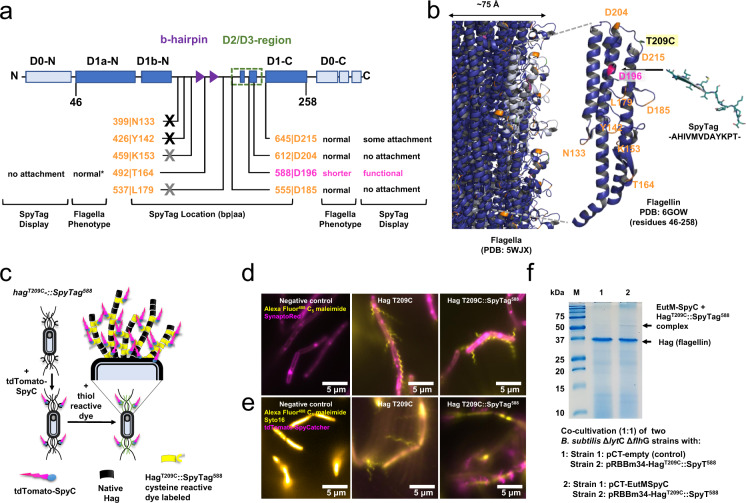
Fig. 4. Engineering of flagella for SpyTag display.
a A SpyTag sequence was inserted at different locations in the hypervariable regions of the flagellin protein (encoded by hag). Shown are conserved domains, including the solvent-exposed D2/D3 domains58. The SpyTag insertions (orange & magenta labels indicate bp and residue locations, magenta denotes functional site) had different impacts on flagella phenotypes and SpyTag display in both B. subtilis 168 (WT) and B. subtilis ΔlytC ΔflhG expressing plasmid born hagT209C::SpyTagxxx. Except for less curved flagella observed for B. subtilis 168 compared to normal (indicated by *) flagella for B. subtilis ΔlytC ΔflhG, phenotypes were the same between the two strains. Several hag insertion mutants could not be transformed into either strain and seem to be lethal (black cross) when expressed in trans of the genomic hag copy. Gray cross: hag mutants could only be transformed into B. subtilis ΔlytC ΔflhG but recovered plasmids were mutated. No or some attachment: modified flagella could not or only be weakly labeled with tdTomato SpyCatcher. b Flagellar filament and flagellin structures82 show locations of the SpyTag insertions (orange & magenta, corresponding to labels in a) and T209C mutation (yellow box) for dye staining. SpyTag structure (PDB: 4MLI) and sequence are shown for reference. c Flagella assemble from genomic flagellin and plasmid born flagellin (HagT209CSpyTagxxx) subunits. Engineered flagellins are stained with a cysteine reactive dye (Alexa FluorTM 488 C5 maleimide) and functional SpyTag display was tested by growing cultures with purified tdTomato-SpyCatcher protein. d Fluorescence imaging of B. subtilis ΔlytC ΔflhG transformed with pCT-empty (control), pRBBm34-HagT209C or pRBBm34-HagT209C::SpyT588 show that expression of hagT209C::SpyTag588 results in shortened, clustered, polar flagella. Cells are stained and images false-colored as indicated. See Supplementary Fig. 9 for other SpyTag positions. e Functional SpyTag display by HagT209C::SpyTag588 was confirmed by growing strains in the presence of purified tdTomato-SpyCatcher. (Images generated for each strain in d and e are representative of cultures selected from three biological replicate cultures.) f In situ attachment of secreted EutM-SpyCatcher to SpyTags displayed on flagella of B. subtilis ΔlytC ΔflhG was verified by co-cultivation. SDS-PAGE analysis of extracted flagella shows a faint band with the expected size of 55 kDa for a EutM-SpyCatcher (21.1 kDa) and HagT209C::SpyTag588 (34.1 kDa) protein complex in co-cultures secreting EutM-SpyCatcher. Genomic flagellin (32.6 kDa) is the major protein. Shown data is from a single experiment. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.