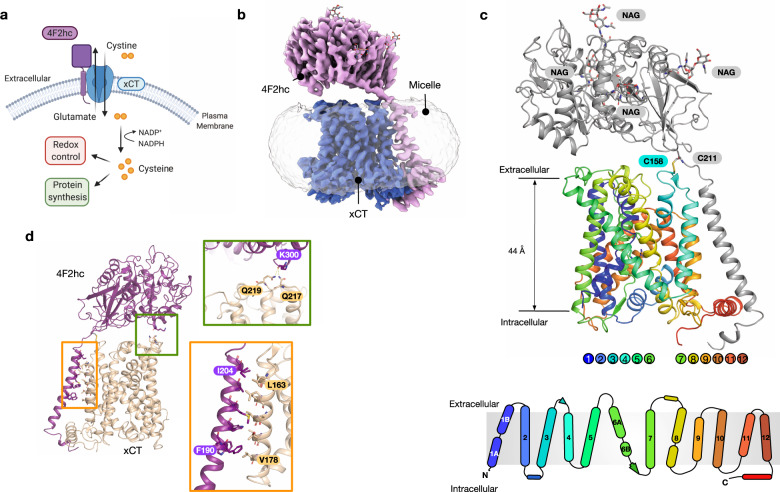
Fig. 1. Cryo-EM structure of system xc−.
a System xc− consists of a heavy chain component, 4F2hc (SLC3A2) and a transport module, xCT (SLC7A11), and functions as a dedicated cystine import system, exchanging extracellular l-cystine for intracellular l-glutamate. Following l-cystine transport into the cell, the molecule is rapidly reduced to l-cysteine via cystine reductase and used to regulate cellular redox levels via glutathione, alternatively free cysteine can also enter the protein synthesis pathway. b Cryo-EM density of 4F2hc (magenta) and xCT (blue) contoured at a threshold level of 1.0, superposed with lower-contoured threshold level of 0.22 to display the detergent micelle (grey). c Cartoon representation of system xc−, with 4F2hc (grey) showing conserved N-linked glycans (NAG). xCT is coloured blue from the N-termini to red at the C-terminus. The cysteines forming the disulphide which connects the two components are also indicated. A topology diagram is also shown of SLC7A11, using the same colours as in the main panel. d Analysis of the interactions between 4F2hc and xCT. The zoomed in views show the interactions between the extracellular domain (green box) and transmembrane domains (orange box).