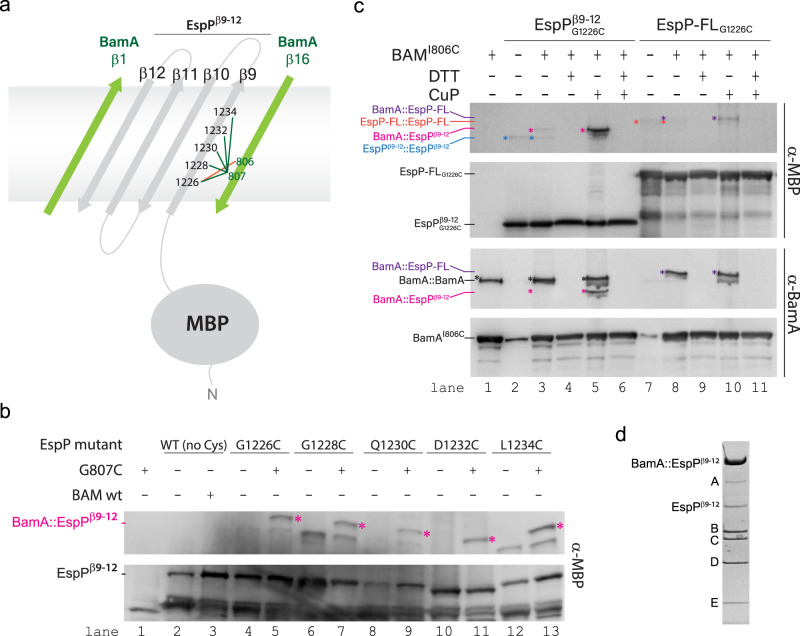
Fig. 7. In vivo screening for the BAM/MBP-EspPβ9–12 intermediate complex.
a Schematic depicting the experimental design for the isolation of the BAM/MBP-EspPβ9–12 intermediate complex. Crosslinking initially focused on residue 807 of β16 of BamA to residues 1226, 1228, 1230, 1232, and 1234 of β9 of EspP (green lines). The final crosslink leading to the high resolution structure was for residue 806 of BamA and residue 1226 of β9 of EspP (orange line). b Using a dual expression system, formation of the BAM/MBP-EspPβ9–12 intermediate was monitored by SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis, with the crosslinked intermediate observed as a high molecular weight band (magenta). The crosslink at residue 1226 of EspP was purified for structure determination. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. c To optimize the stability of the crosslinked intermediate for structure determination, an additional crosslink was prepared on residue 806 of β16 of BamA with residue 1226 of β9 of EspP. SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis using α-MBP and α-BamA antibodies demonstrates that this crosslink forms in full length (FL)-EspP (lanes 8 and 10), yet more efficiently in the truncated construct (lanes 3–5). The crosslinks were enhanced by washing cells with copper o-phenanthroline (CuP) and reduced using DTT. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. d The BAM/MBP-EspPβ9–12 crosslinked intermediate was purified by Ni-NTA and MBPTrap and verified by SDS-PAGE by the presence of the higher molecular weight BamA/EspPβ9–12 crosslinked species. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.