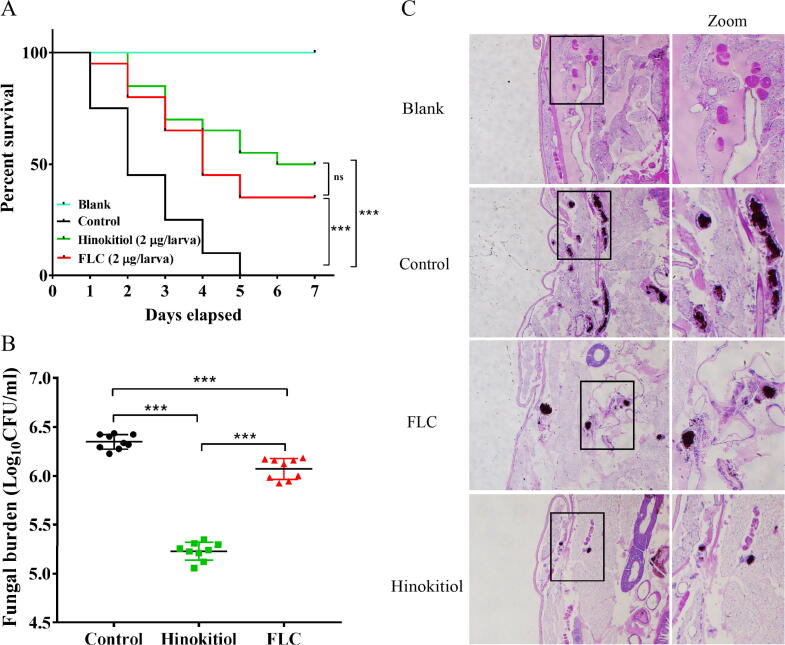
Fig. 6.
Hinokitiol has therapeutic effects on C. albicans-infected G. mellonella. The larvae in each group were infected with at 2 × 105C. albicans cells. After 2 h of infection, the larvae were treated with PBS (control), FLC (2 μg/larva) or hinokitiol (2 μg/larva). The larvae in blank group were not infected but injected with equal volume of PBS. (A) Survival curve of infected G. mellonella by C. albicans (n = 20 per group). The number of surviving larvae was recorded each day. The Mantel-Cox test was used to compare differences between the groups. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. ns means non-significance. (B) Fungal burden of infected G. mellonella by C. albicans (n = 9 per group). (C) The larvae in different treated groups (n = 2 per group) were fixed by paraformaldehyde and processed for periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining. The histopathology of infected G. mellonella under different indicated treatments was examined by microscopic inspections. The rectangles highlighted the melanized nodules containing a mixture of yeast cells and filaments for closer observation (right lane).