Figure 3.
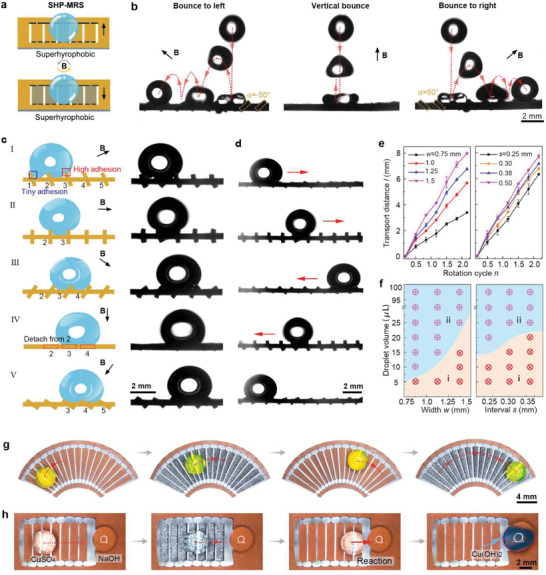
Directional bounce and controllable transport of droplets on SHP‐MRS. a) Schematic of SHP‐MRS under magnetic actuation, whose surfaces are superhydrophobic. b) The bounce behaviors of droplets (6 µL) on SHP‐MRS at swing angles α of −50°, 0°, and 50°, respectively. c) The directional transport of water droplet (18 µL) on SHP‐MRS (w = 1.25 mm, and s = 0.30 mm) under a rotating magnetic field. d) The droplet (18 µL) moves back and forth on SHP‐MRS driven by the clockwise and anticlockwise rotating magnetic field, respectively. e) The effects of rotation cycles n on the transport distance, l, under w of 0.75, 1.0, 1.25, and 1.5 mm and s of 0.25, 0.30, 0.38, and 0.50 mm, respectively. f) The phase diagram revealing the transportation capability of SHP‐MRS under different widths and intervals of the microblades. The region (i) represents the failure of droplet transport in which droplets gets stuck between the intervals of the microblades, while the region (ii) represents the success of droplet transport. g) The fan‐shaped SHP‐MRS (w = 0.65–1.4 mm,and s = 0.30–0.50 mm) delivers the droplet (30 µL) in an arc pathway. h) Demonstration of SHP‐MRS (w = 1.25 mm, and s = 0.30 mm)‐ based microreactor. The CuSO4 droplet (30 µL) is delivered to react with NaOH droplet, and blue Cu(OH)2 precipitates are synthesized.
