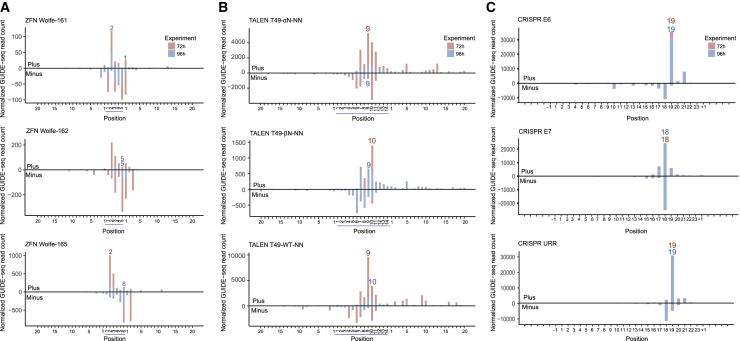
Figure 2.
Distribution of GUIDE-seq reads start positions for on-target sites of ZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPRs
Red shows experiments at 72 h; blue shows experiments at 96 h. (A) Distribution of GUIDE-seq read counts for ZFN Wolfe-161, ZFN Wolfe-162, and ZFN Wolfe-165’s on-target sites. Bars above and below the x axis refer to reads aligned to the plus strand and minus strand, respectively. The displaying window covers both the spacer (underlined in blue) and flanking sequences. The numeral positions were reranked from 1 in the start of the spacer, left and right ZFP. The most frequent dsODN integration positions are marked. (B) Distribution of GUIDE-seq reads start for T49-αN-NN, T49-βN-NN, and T49-WT-NN on-target sites. The displaying window covers both the spacer (underlined in blue) and 20-bp flanking sequences. The numeral positions were reranked from 1 in the start of the spacer, left and right TALE. The most frequent dsODN integration positions are marked. (C) Distribution of GUIDE-seq read counts for CRISPR E6, CRISPR E7, and CRISPR URR on-target sites. The displaying window covers both the 23-bp target and the 5-bp flanking sequences. The most frequent dsODN integration positions are marked.