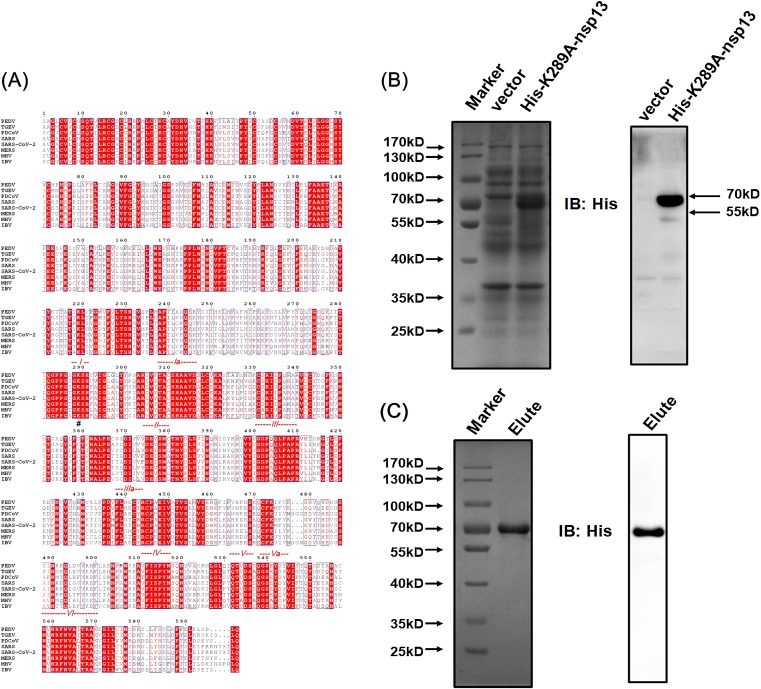
Fig. 5.
Expression and purification of the nsp13-K289A mutant. (A) Sequence alignments of nsp13 from different coronaviruses. Alignment was generated in ESPript 3.0 (http://espript.ibcp.fr/ESPript/cgi-bin/ESPript.cgi), and the nsp13 sequences of transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) strain Purdue 46 (accession number AJ271965), porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) isolate CHN-HN-2014 (accession number KT336560), SARS-CoV isolate Frankfurt 1 (accession no. AY291315), MERS-CoV isolate Al-Hasa_7a_2013 (accession number KF600655), murine hepatitis virus (MHV) strain JHM (accession number AC_000192), avian infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) strain Beaudette (accession number NC_001451.1) and SARS-CoV-2 isolate Wuhan-Hu-1 (accession number NC_045512.2) were derived from GenBank. The red dotted lines indicate conserved helicase motifs I–VI. “#” indicates the conserved K289 residue. (B, C) The expressed (B) or purified (C) nsp13-K289A recombinant proteins were analyzed by electrophoresis on 10 % SDS-PAGE, then stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (left) or western blotted with anti-His antibody (right).