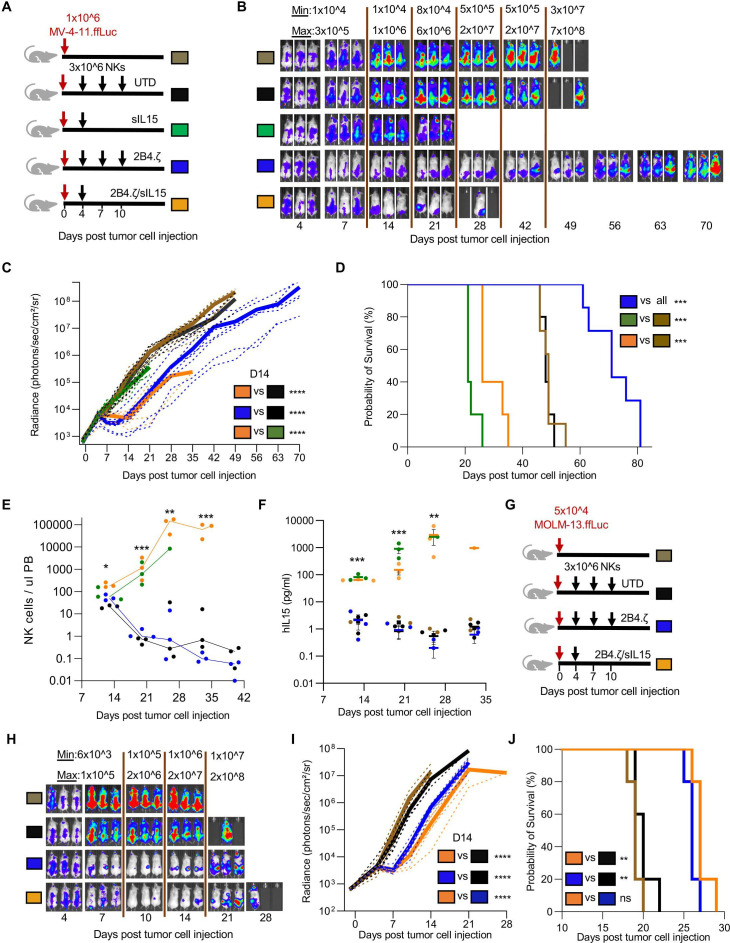
Figure 6.
IL-15 secreting CAR-NK cells can cause lethal toxicity in an AML xenograft model. (A) Schematic of NK-cell dosing in MV-4-11.ffLuc model. (B) MV-4-11 proliferation was monitored with BLI. Representative images of mice. The minimum and maximum values of the color scale are indicated (min–max). (C) BL representative of leukemia proliferation was recorded as photons/s/cm²/sr. Dotted lines: individual mice; solid lines: mean (n=5–7 mice per group; two experiments performed for UTD and 2Β4.ζ cohorts). (D) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. (E) Mouse PB was collected at indicated time points and analyzed via flow cytometry. NK-cell numbers per microlitre of mouse PB were tracked starting on D13 of the experiment. Each dot represents cell numbers from a single mouse; line is at median. Asterisks indicate 2B4.ζ/sIL-15 versus 2Β4.ζ comparison. (F) Human IL-15 from PB of MV-4-11 engrafted mice drawn at the indicated time points was quantified (pg/mL) with ELISA. Asterisks indicate 2B4.ζ/sIL-15 versus 2Β4.ζ comparison. (G) Schematic of NK-cell dosing in MOLM-13.ffLuc model. (H) MOLM-13 proliferation was monitored using BLI (n=5 mice per group). Representative images, (I) radiance, and (J) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. AML, acute myelogenous leukemia; BLI, bioluminescence imaging; CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; D, day; ffLuc, firefly luciferase; IL, interleukin; NK, natural killer; PB, peripheral blood; sIL, secretory interleukin; UTD, untransduced.