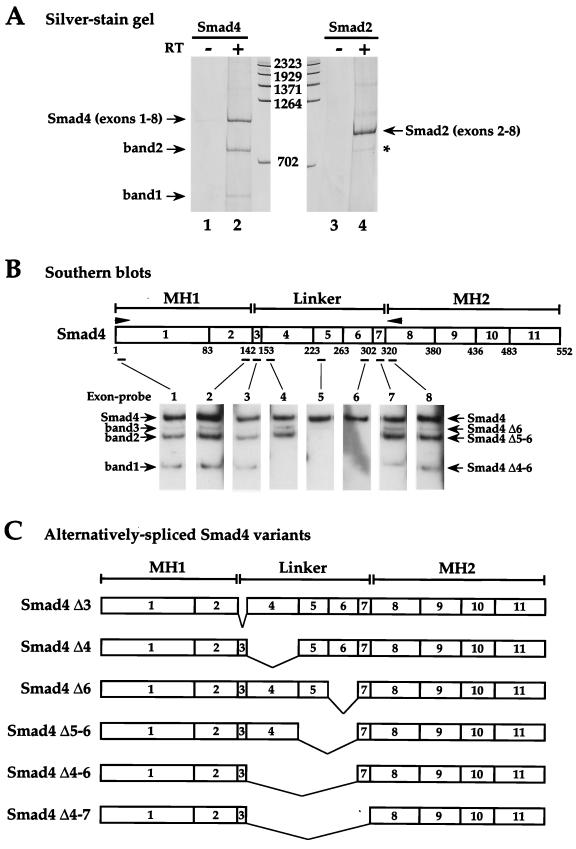
FIG. 1.
Human Smad4 mRNA is alternatively spliced. (A) Silver-stained polyacrylamide gel showing fragments obtained from RT-PCRs performed using total RNA from HaCaT cells as template and forward and reverse primers specific for exon 1 and exon 8, respectively, of human Smad4 (lanes 1 and 2) or exon 2 and exon 8, respectively, of human Smad2 (lanes 3 and 4). The reactions in lanes 1 and 3 were performed with no reverse transcriptase. DNA markers are measured in base pairs. The fragment derived from full-length Smad4 is designated Smad4 (exons 1-8), and that derived from full-length Smad2 is designated Smad2 (exons 2-8). Bands 1 and 2 are derived from alternatively spliced Smad4 mRNA. The asterisk denotes the Smad2 alternatively spliced variant (Smad2 Δexon 3) (49). (B) Identification of Smad4 isoforms by Southern blotting. A diagram of the Smad4 coding region is shown, denoting the MH1, linker, and MH2 domains. Arrowheads show PCR primers used in the RT-PCR. Exons are denoted as boxes with the exon numbers indicated. Numbers below are amino acids at the exon-intron boundaries (13). Positions of the oligonucleotide exon-specific probes are indicated. RT-PCR products similar to that in lane 2 above were Southern blotted with exon-specific probes as indicated. The bands 1 and 2 are as described above; band 3 is detected only by Southern blotting. The bands are identified as Smad4 Δ4-6, Δ5-6, and Δ6, respectively. (C) Schematics of the alternatively spliced Smad4 isoforms identified.