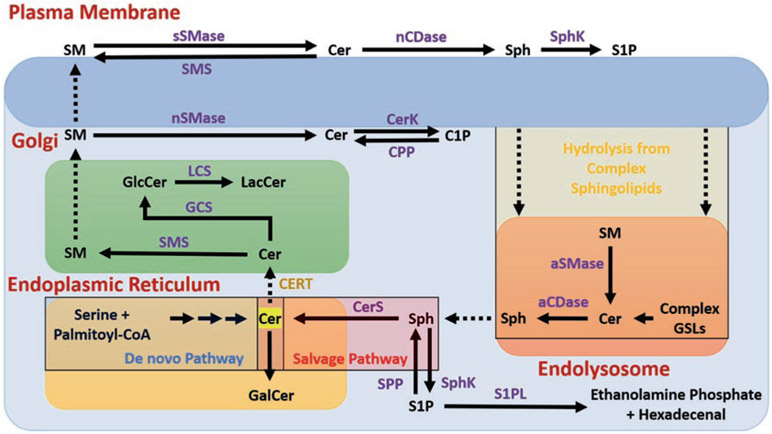
Fig. 8.1.
Schematic representation of cellular sphingolipid metabolism. Ceramide (Cer) is produced primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) from serine and palmitoyl-CoA via a series of reactions in the de novo pathway. Cer is then either converted to Galactosylceramide (GalCer) by addition of a galactose or transported from the ER to the trans-Golgi, possibly via a trafficking mechanism mediated by Cer Transfer Protein (CERT). In the Golgi, Cer is either converted to Sphingomyelin (SM) by Sphingomyelin Synthase (SMS), or is glycosylated to form Glucosylceramide (GlcCer) by GlcCer Synthase (GCS). GlcCer may be converted to Lactosylceramide (LacCer) by addition of galactose with LacCer Synthase (LCS). SM from the Golgi is transported to the plasma membrane, where it may be converted by cytosolic neutral sphingomyelinase (nSMase) back to Cer, which is phosphorylated by Cer Kinase (CerK) to ceramide 1-phosphate (C1P). Alternatively, SM may be converted to Cer via secretory SMase (sSMase), which is converted to Sphingosine (Sph) by neutral ceramidase (nCDase). Sph is phosphorylated to sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) by Sphingosine Kinase (SphK) 1 or 2, which can signal extracellularly via membrane-bound S1P receptors (of which there are 5 known). Complex sphingolipids from the plasma membrane may enter the endolysosomal pathway and be hydrolyzed back to Cer, which is converted to Sph within the lysosome by acid ceramidase (aCDase or ASAH1, N-Acylsphingosine Amidohydrolase 1). From here, Sph is either phosphorylated to S1P or re-acylated back to Cer by Ceramide Synthase (CerS) in the salvage pathway. S1P leaves the sphingolipid metabolic pathway by conversion to ethanolamine phosphate and hexadecenal by Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Lyase (S1PL)