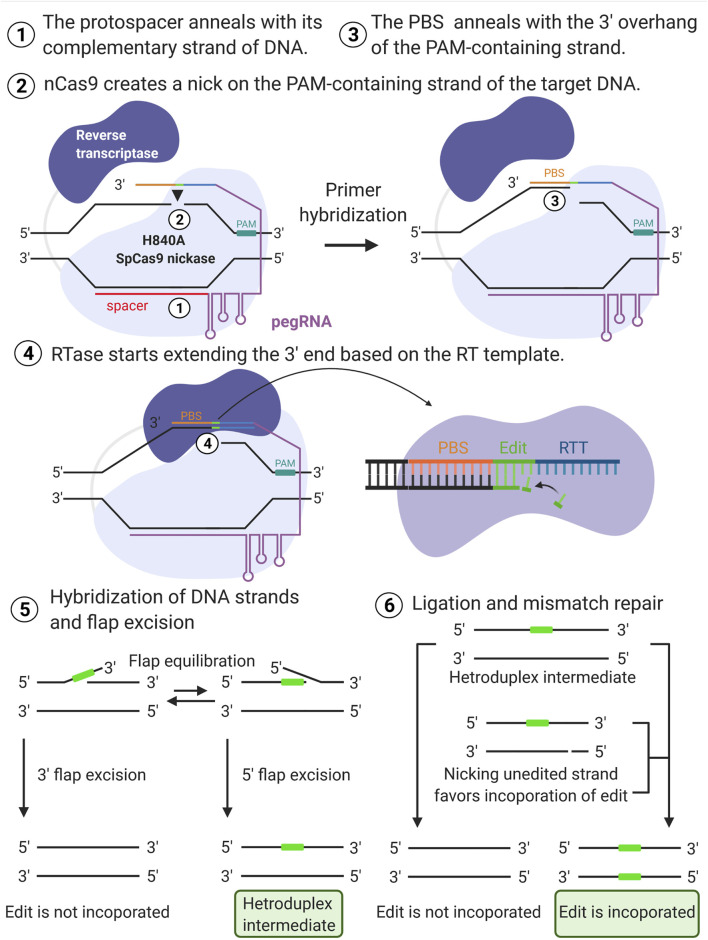
FIGURE 2.
Overview of prime editing mechanism. The spacer (red line) anneals with its complementary strand of the DNA (1) directing the H840A SpCas9 nickase to nick the PAM-containing strand (black arrow) of the target DNA (2). The primer binding sequence (PBS) then hybridizes with the nicked DNA (3) initiating the elongation of the free 3′ end according to the reverse transcription template (RTT) sequence that carries the intended edit (4). The newly synthesized strand leads to either 3′ or 5′ flap excision. The excision of the 5′ flap is favored, and it leads to the heteroduplex formation (5). The replacement of the original sequence via endogenous DNA mismatch repair mechanism incorporates the desired mutation at the target site (6). “Created with BioRender”.