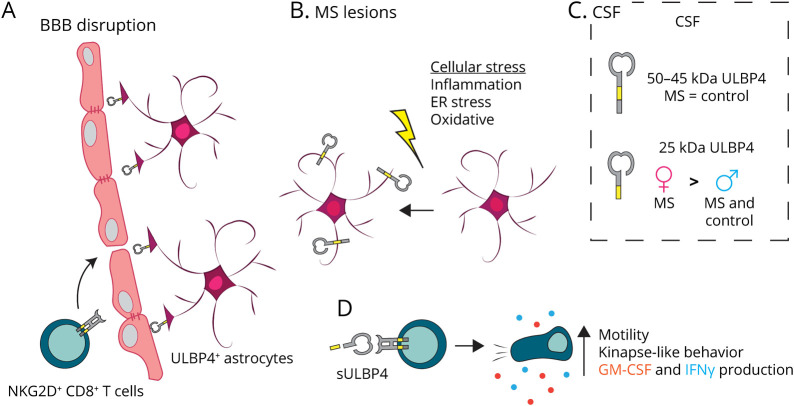
Figure 6. Proposed Involvement of the NKG2D Pathway in MS Pathology.
(A) CD8+ T lymphocytes can enter the CNS of patients with MS in part due to disrupted BBB. All infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes express NKG2D7 and thus can interact with ULBP4-expressing astrocytes including those having end feet in close proximity to the BBB. (B) Various cellular stresses (inflammation, ER stress, and oxidative stress) present in the brain of patients with MS can upregulate ULBP4 expression by astrocytes, as supported by our in vitro data. Reactive astrocytes, which are abundantly present in MS lesion, represent the predominant cell type expressing ULBP4 in the brain of patients with MS. (C) Soluble forms of ULBP4 are detectable in CSF; a soluble 25-kDa ULBP4 form is significantly elevated in CSF from female patients with MS compared with groups (male patients with MS and controls of both sexes). (D) Soluble ULBP4 can affect immune cell functions. On contact with sULBP4, CD8+ T lymphocytes increase their secretion of GM-CSF and IFNγ. Moreover, addition of sULBP4 to CD8+ T lymphocytes cocultured with astrocytes increases their motility and favors kinapse-like behaviors, which are more dynamic and may lead to enhanced displacement within the tissue. BBB = blood-brain barrier; ER = endoplasmic reticulum; MS = multiple sclerosis; sULBP4 = soluble UL16-binding protein 4.