Fig. 3. Brain MR imaging.
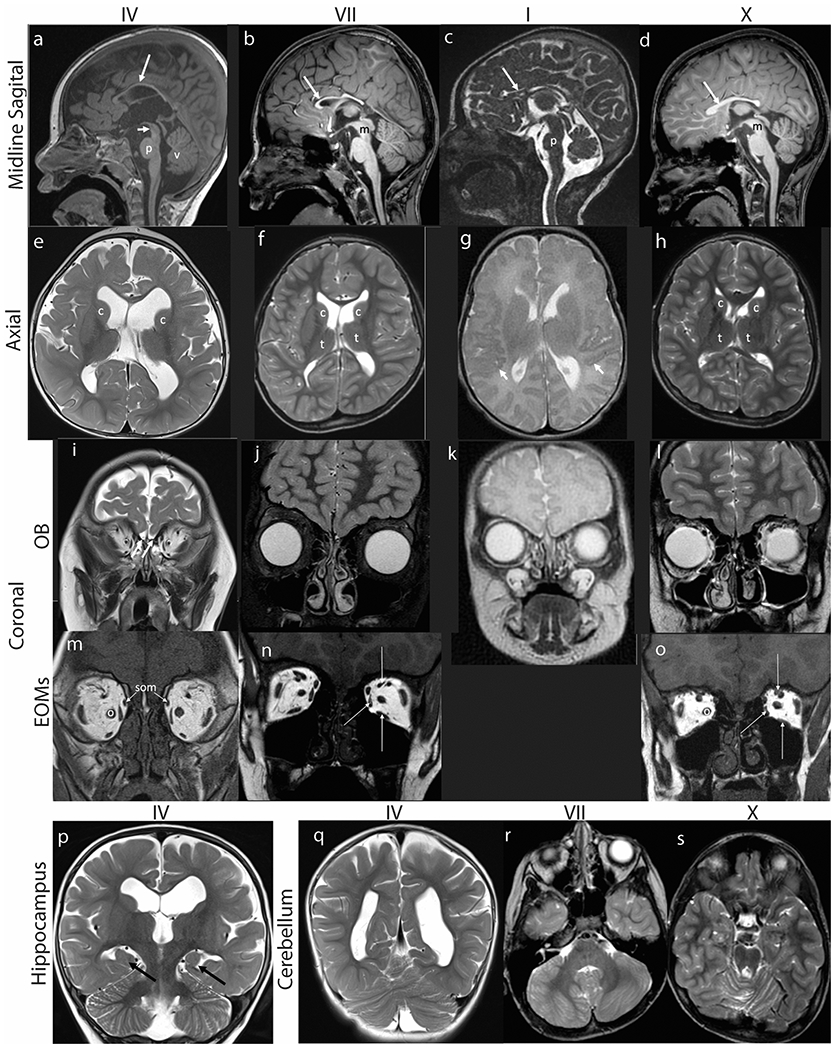
Hypoplasia of corpus callosum, dysmorphic basal ganglia, absence of olfactory bulbs, small extraocular muscles, incomplete hippocampal inversion, and cerebellar abnormalities in subjects IV (a,e,i,m,p,q), VII (b,f,j,n,r), I (c,g,k) and X (d,h,l,o,s). (a-d) Midline sagittal T1 weighted (a, b, d) or FIESTA (c) images demonstrate marked thinning of the corpus callosum (long arrows). (a) The pons (p) appears mildly shortened in height and narrowed in AP diameter. The tegmentum of the midbrain (short arrow) appears slightly thinned and elongated. There is slight uplifting of the vermis (v). (b) The pons is minimally narrowed in AP diameter with slightly accentuated dorsal indentation and the distal midbrain (m) tegmentum is thinned. (c) The pons (p) is hypoplastic, appearing shortened in height and anteroposterior diameter with accentuated dorsal indentation. The vermis is slightly uplifted but normal in size. (d) There is mild thinning of the distal midbrain (m) and the pons is minimally shortened in height with accentuated dorsal indentation. (e-h) Axial T2 weighted MR images of the brain demonstrate asymmetry of the lateral ventricles and dysmorphic basal ganglia. (e) The caudate nuclei (c) and basal ganglia are asymmetric in shape and position, with the left caudate head more dorsally positioned than the right. The white matter appears mildly decreased in thickness. The lateral ventricles are prominent. (f) The caudate heads (c) are asymmetric with the left appearing shorter and wider. Mildly asymmetric shape and positioning of the thalami (t). The Sylvian fissures are asymmetric with the left shorter in length than right. The parietal and right frontal white matter appears mildly decreased in thickness with a small focus of high signal intensity adjacent to the right lateral ventricular atrium. (g) The perisylvian cortex has a serrated appearance raising concern for polymicrogyria (short arrows). (h) The lateral ventricles, caudate heads (c) and thalami (t) are asymmetric in shape. Mildly decreased thickness of right frontal and left > right parietal periventricular white matter. (i-l) Coronal MR images at the level of the cribriform plates (white arrows in I) reveal absent olfactory bulbs and sulci with only small vessels visible. (m-o) Coronal T1 weighted MR images show small medial, superior, and inferior rectus muscles (long white arrows in N and O). The superior oblique muscles (som, arrows, M) are also small and inferomedially positioned. The optic nerves (o) appear medialized. (p-q) Coronal T2 weighted MR images of the brain show (P) incomplete hippocampal inversion bilaterally (black arrows). The 3rd and lateral ventricles are moderately dilated with the left lateral ventricle appearing larger than the right. The body of the left caudate nucleus appears smaller than the right (c), and more inferolaterally positioned. (q) The cerebellum appears mildly rotated. (r) Axial T2 weighted MR image at the level of the posterior fossa shows asymmetric architecture of the cerebellar hemispheres with generalized mild dysmorphism on the right. There is minimal disorganization of the superior cerebellar vermian folia. (s) Axial T2 weighted images show minimal dysmorphism of the superior cerebellar vermis.
