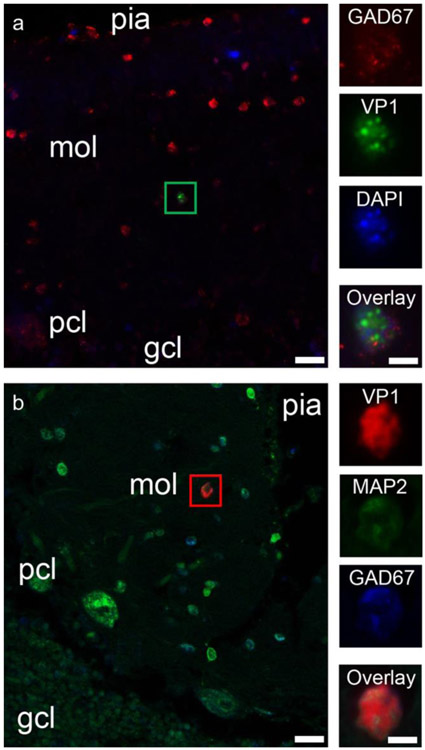
Fig. 2.
JCV infection of interneurons in the cerebellar molecular layer in PML patients. a JCV VP1 expression in an interneuron of the cerebellar molecular layer of a PML patient. Left—Double immunofluorescence image of the cerebellar cortex from a PML patient, shows numerous GAD-67-positive cerebellar cortical interneurons (red), one of which is also immunopositive for VP1 (noted with a green box). Pial surface of the cerebellar cortex is on the top of the image, with the molecular layer (mol), Purkinje cell layer (pcl), and granule cell layer (gcl) as indicated in the deeper layers. Scale bar = 20 μm. Right column—Higher magnification image of the interneuron marked with the green box. Panels show GAD67 immunopositivity (red), VP1 immunopositivity (green), nuclear staining (DAPI in blue), and then all three channels overlaid (Overlay). Scale bar = 5 μm. b JCV VP1 expression in an interneuron of the cerebellar molecular layer of a PML patient. Pial surface of the cerebellar cortex is on the top right of the image, with the molecular layer (mol), Purkinje cell layer (pcl), and granule cell layer (gcl) as indicated in the deeper layers. Scale bar = 20 μm. Right column—Higher magnification image of the interneuron marked with the green box. Panels show JCV VP1 immunopositivity (red), MAP2 immunopositivity (green), and GAD67 immunopositivity (red), and then all three channels overlaid (Overlay). Scale bar = 5 μm