Fig. 1 |. Overview of rare genetic disorders (RGDs).
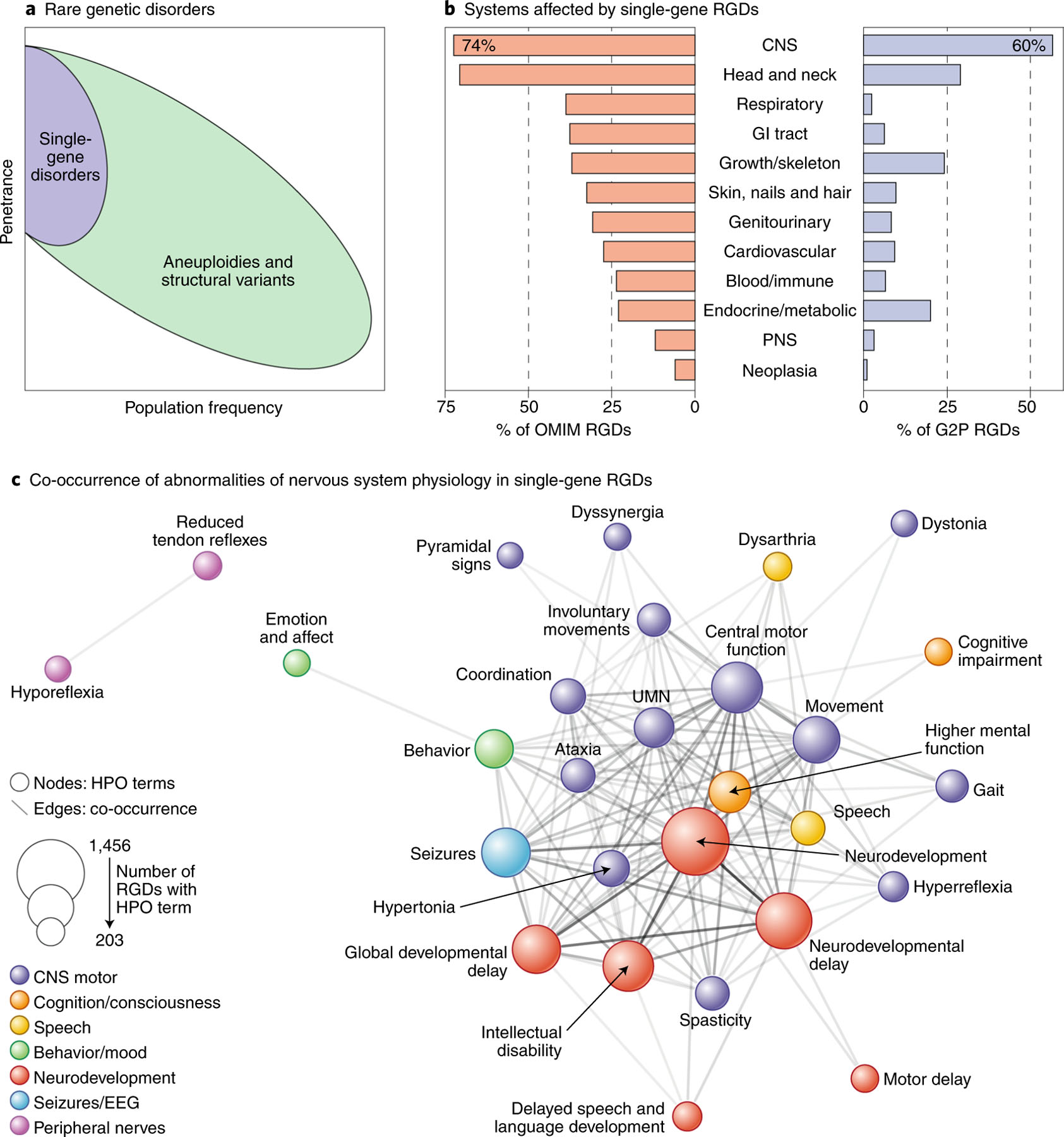
a, RGDs may be caused by variants that affect one gene (purple) or many genes (green). Many aneuploidies and structural variants arise spontaneously at higher rates than single-gene disorders, leading to comparatively high population frequencies for a given penetrance33,124. b, The CNS is involved in the majority of single-gene RGDs. c, Single-gene RGDs frequently affect multiple neuropsychiatric domains, as shown by extensive co-occurrence of Human Phenotype Ontology terms (Supplementary Table 1)125. Terms that co-occur in at least 200 RGDs are shown as nodes (colored circles, size determined by the number of RGDs), with edge weight (gray lines) determined by the degree of co-occurrence of a term between RGDs (203–1,114). Network layout is based on the Compound Spring Embedder algorithm126. OMIM, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man; G2P, Gene2Phenotype; HPO, Human Phenotype Ontology; CNS, central nervous system; PNS, peripheral nervous system; UMN, upper motor neuron. Credit: Debbie Maizels/Springer Nature.
