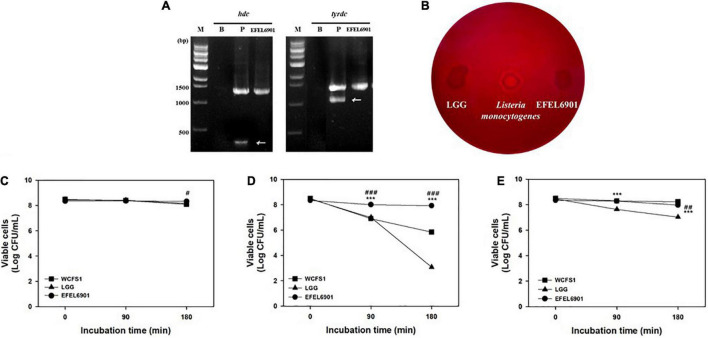
FIGURE 1.
Safety and stability assessment of Limosilactobacillus reuteri EFEL6901 strains. (A) Detection of genes related to biogenic amine production. Lane M, 1 kb DNA marker; lane 1, negative control which has no template DNA; lane 2, positive controls having hdc (histidine decarboxylase, 440 bp), and tyrdc (tyrosine decarboxylase, 1100 bp) genes from L. reuteri ATCC 23272 and Enterococcus faecalis KCCM 11729, respectively. (B) Hemolytic activity analysis of L. reuteri EFEL6901. Hemolytic activity was measured in BHI broth containing 7% horse blood. Left, the negative control, L. rhamnosus GG; center, positive control, Listeria monocytogenes; right, the EFEL6901 strain, showing clear zone around the cell drop. (C) Viability of L. reuteri EFEL6901 at pH 3.0. (D) Viability of L. reuteri EFEL6901 at pH 2.5. (E) Viability of L. reuteri EFEL6901 in 0.3% bile salt. Significant differences are presented with L. plantarum WCFS1 (#p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, and ###p < 0.001) or L. rhamnosus GG (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001).