Figure 2. Functional characterization of Aldh1a1.
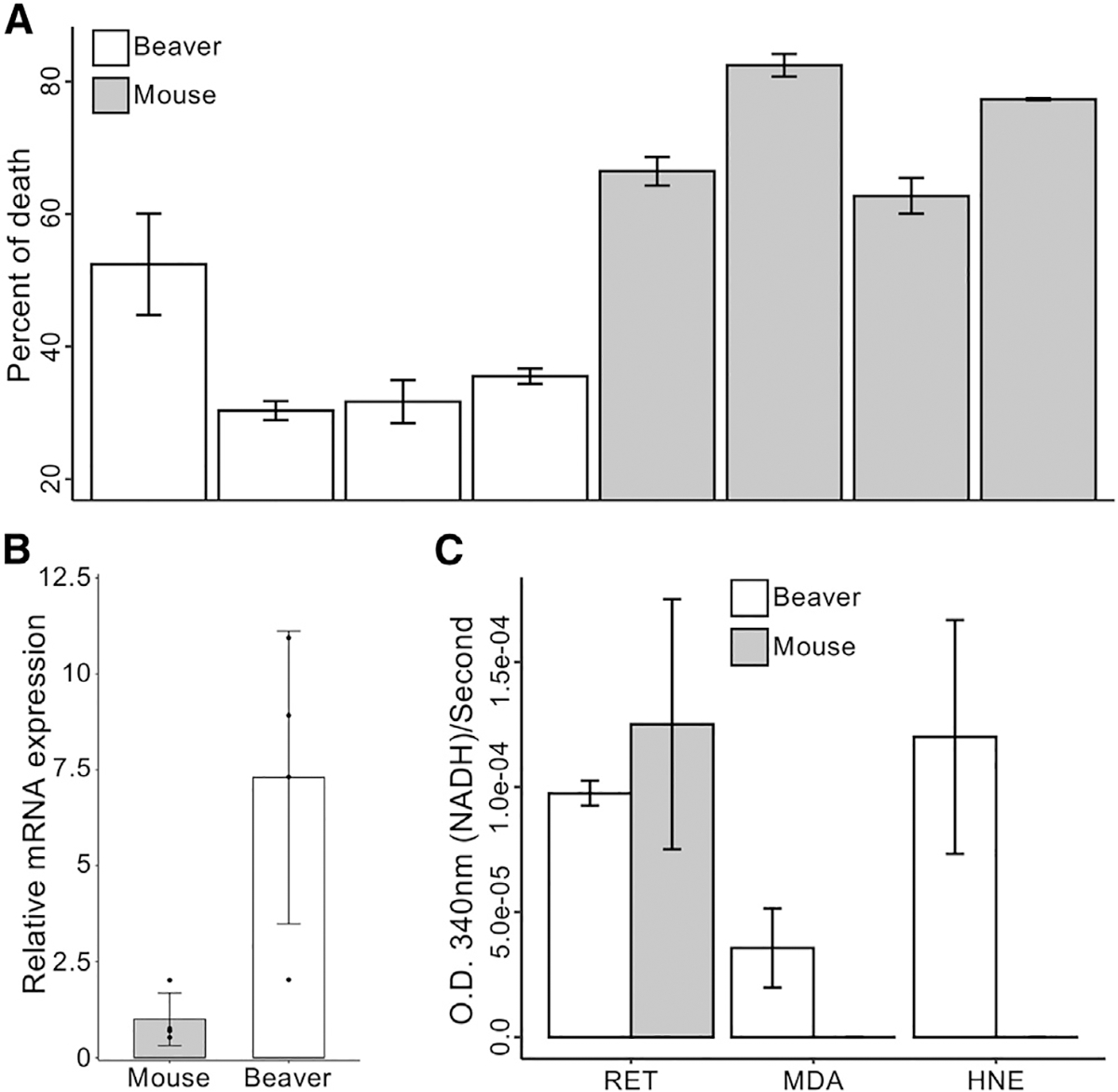
(A) Cell viability. Beaver lung fibroblasts have a lower percentage of death in the presence of high concentrations of ethanol, normalized by corresponding controls (p = 0.002 by mixed-effects model; see Method details).
(B) Expression of Aldh1a1 in lung fibroblasts measured by qPCR with β-actin normalization. The expression of Aldh1a1 in beaver cells is higher than in mouse cells (p = 0.02, 1-tailed t test).
(C) Aldehyde metabolic activity. Enhanced Aldh1a1 activity of beaver in aldehyde metabolism. Activities are normalized by corresponding controls without any addition (see Method details). HNE, 4-hydroxynonenal; MDA, malonaldehyde; RET, all-trans-retinal.
Lung fibroblasts were used in experiments of (A) and (B). Cytosolic extracts from hepatocytes were used for the experiment of (C). Four different biological samples of each species were used in experiments of (A)–(C), with 3 technical replicates of each sample for (A) and (C), and 2 technical replicates of each sample for (B). Data are shown as mean ± SD.
