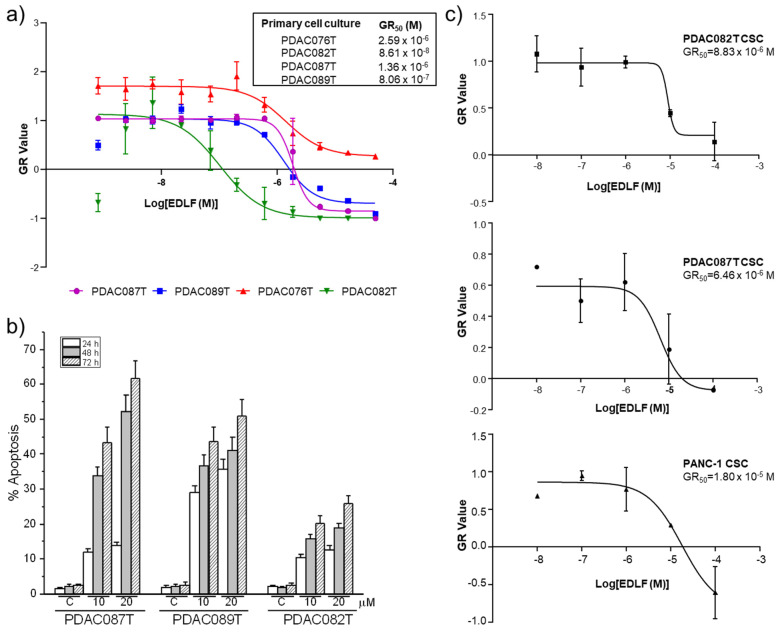
Figure 7.
Characterization of the chemosensitivity profile after edelfosine treatment in human pancreatic cancer primary cultures. (a) Four different PDAC-derived primary cell cultures were treated with increasing concentrations of edelfosine (EDLF), and the ability to inhibit cell proliferation was measured after 72 h of treatment. The growth inhibition rate was calculated applying the GR metrics R package. The data represent the means ± SD of the GR metric scores. GR50 values for each pancreatic cancer primary culture are shown (inset). (b) Induction of apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer primary cultures by edelfosine treatment. PDAC087T, PDAC089T and PDAC082T were incubated with 10 and 20 μM edelfosine for the indicated incubation times, and the percentage of apoptosis was then determined by means of flow cytometry, as assessed by the increase of cells in the sub-G0/G1 region. Untreated control cells were run in parallel. The data are shown as the means ± SD of three independent experiments. (c) Effect of edelfosine on the proliferation capacity of CSC pancreatic cancer spheroids generated from PDAC082T, PDAC087T and PANC-1. The cells were incubated with different concentrations of edelfosine for 72 h. Growth inhibition was analyzed by using the GR metrics as above, and the GR50 values are shown. The results shown are the means ± SD of three independent experiments performed in triplicate.