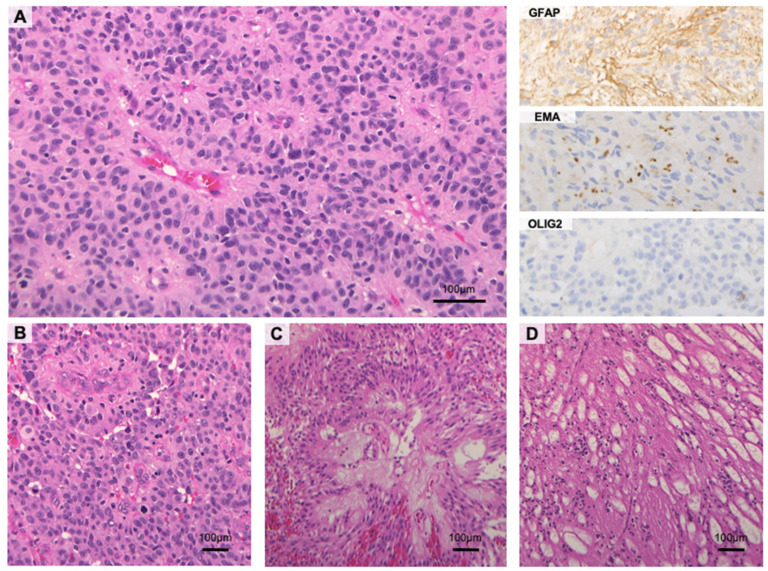
Figure 1.
Histological features of ependymal tumors. (A) Classic ependymomas are well-circumscribed neoplasms with clear-cut vascular pseudorosettes. Immunohistochemically, the neoplastic cells show variable expression for GFAP with characteristic para-nuclear dot-like positivity for EMA. OLIG2 is weak to negative (B) Anaplastic ependymomas are hypercellular tumors with brisk mitotic activity, frequent micro-vascular proliferation, and palisading necrosis. (C) Myxopapillary ependymomas feature well-differentiated cuboidal to elongated tumor cells that are radially oriented around vascularized myxoid cores with a papillary architecture. Endothelial proliferation and cellular atypia are typically absent. (D) Subependymomas consist of small clusters of cells with isomorphic nuclei, scattered throughout a finely fibrillary background with microcysts (H and E and immunoperoxidase stains; original magnification, 10×, 20× and 40×).